[转载]C#发现之旅第十二讲 基于反射和动态编译的快速ORM框架 – 袁永福 电子病历,医疗信息化 – 博客园.
系列课程说明
 为了让大家更深入的了解和使用C#,我们将开始这一系列的主题为“C#发现之旅”的技术讲座。考虑到各位大多是进行WEB数据库开发的,而所谓发 现就是发现我们所不熟悉的领域,因此本系列讲座内容将是C#在WEB数据库开发以外的应用。目前规划的主要内容是图形开发和XML开发,并计划编排了多个 课程。在未来的C#发现之旅中,我们按照由浅入深,循序渐进的步骤,一起探索和发现C#的其他未知的领域,更深入的理解和掌握使用C#进行软件开发,拓宽 我们的视野,增强我们的软件开发综合能力。
为了让大家更深入的了解和使用C#,我们将开始这一系列的主题为“C#发现之旅”的技术讲座。考虑到各位大多是进行WEB数据库开发的,而所谓发 现就是发现我们所不熟悉的领域,因此本系列讲座内容将是C#在WEB数据库开发以外的应用。目前规划的主要内容是图形开发和XML开发,并计划编排了多个 课程。在未来的C#发现之旅中,我们按照由浅入深,循序渐进的步骤,一起探索和发现C#的其他未知的领域,更深入的理解和掌握使用C#进行软件开发,拓宽 我们的视野,增强我们的软件开发综合能力。
课程说明
在上次课程中,我们使用.NET框架提供的特性和反射来创建了一个简单的ORM框架,在这个框架中,由于频繁的进行比较慢的反射操作,因此ORM框架运行速度比较慢,在操作大批量的数据时性能比较差。在本次课程中我们在原先的基础上加上动态编译的技术来实现快速ORM框架。快速ORM框架将不会有性能问题。点击下载本课程的C#2005的演示代码 http://files.cnblogs.com/xdesigner/MyFastORM.zip 。
动态编译技术
所谓动态编译技术就是应用程序在运行时,程序内部自动的生成C#代码,然后调用.NET框架提供的C#程序编译器生成临时的程序集,然后将临时程序集加载到应用程序域中动态的调用其中的对象模块。
动态编译技术内部调用了代码生成器。以前我们是在编程时使用代码生成器生成代码文档,然后添加到C#工程中,然后进行整体编译,此时我们是手工的使用代码生成器,这个过程可以称为静态编译。而动态编译技术却是将这个过程自动化了,而且调用代码生成器生成代码文本的过程放置在软件运行时执行。
动态编译技术能同时兼顾灵活性和性能。微软.NET框架本身也有动态编译技术的应用,比如XML序列化和反序列化,ASP.NET框架处理ASPX文件等等。
一般而言使用动态编译技术的过程可以为
1. 应用程序需要调用动态编译功能,则收集一些参数,然后调用动态编译模块。
2. 动态编译模块内部有一个全局的临时编译的程序集的缓存列表,若根据应用程序传递的参数可以在缓存列表中找到相匹配的临时程序集则直接返回这个程序集对象。
3. 动态编译模块收集参数,然后调用内置的代码生成器生成代码字符串。
4. 动态编译模块调用微软.NET框架提供的C#代码编译器,生成一个临时的程序集对象。具体就是调用Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider 提供的方法。在这个过程中,程序将会在磁盘上生成若干临时文件,这个过程会受到微软.NET框架的安全设置的影响。
5. 将临时编译生成的程序集对象保存到全局的临时程序集的缓存列表,然后向应用程序返回这个临时程序集,而应用程序将会使用反射的手段来调用临时程序集提供的功能。

动态编译技术中生成的临时程序集和我们使用开发工具生成的程序集没有差别,运行速度是一样的快。因此动态编译技术除了能实现灵活的功能外还提供良好的性能。
我们要使用动态编译技术,首先得看要实现的功能是否灵活多变,若我们要实现的功能比较简单,使用静态编译技术就足够了,那我们就用不着使用动态编译技术。若功能非常复杂,无法使用代码生成器生成代码来实现它,则也不能使用动态编译技术。
注意,动态编译技术会在磁盘中生成临时文件,因此.NET框架的安全设置会影响到动态编译技术的正常运行,而且使用该技术的程序会生成C#代码并保存到临时文件,然后调用.NET框架的C#代码编译器生成临时程序集,而恶意软件会在这两个步骤间隙迅速的修改C#代码文件并插入恶意代码,对此动态编译技术无法判别。
快速ORM框架整体设计
在这里我们将以上节课的ORM框架为基础,对它进行改造,加入动态编译技术来打造一个快速ORM框架。首先我们还得使用BindTableAttribute和BindFieldAttribute特性来描述实体类型和数据库的绑定信息。于是我们上节课使用的演示用的实体类型DB_Employees就原封不动的用到现在。该实体类型的代码为
System.Serializable()]
[BindTable("Employees")]
public class DB_Employees
{
///
<summary>/// 人员全名/// </summary>
public string FullName
{
get
{
return this.LastName + this.FirstName ;
}
}
#region 定义数据库字段变量及属性 //////////////////////////////////////////
///
<summary>/// 字段值 EmployeeID/// </summary>
private System.Int32 m_EmployeeID = 0 ;
///
<summary>/// 字段值 EmployeeID/// </summary>
[BindField("EmployeeID" , Key = true )]
public System.Int32 EmployeeID
{
get
{
return m_EmployeeID ;
}
set
{
m_EmployeeID = value;
}
}
///
<summary>/// 字段值 LastName/// </summary>
private System.String m_LastName = null ;
///
<summary>/// 字段值 LastName/// </summary>
[BindField("LastName")]
public System.String LastName
{
get
{
return m_LastName ;
}
set
{
m_LastName = value;
}
}
其他字段……………..
#endregion
}// 数据库操作类 DB_Employees 定义结束
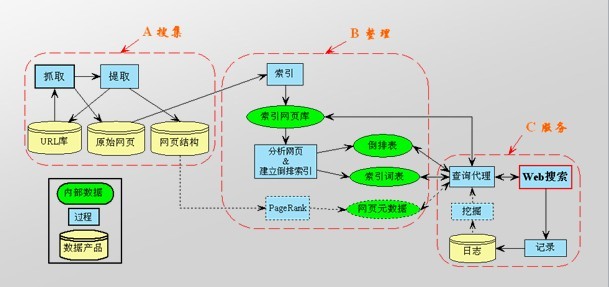
我们设计快速ORM框架的程序结构如图所示
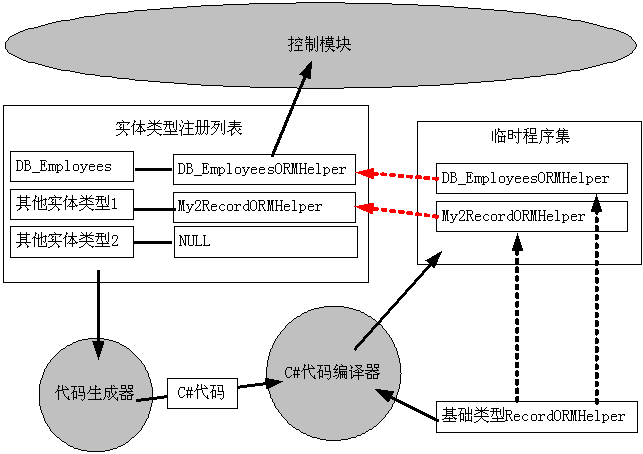
框架中包含了一个实体类型注册列表,列表中包含了实体类型和相应的RecordORMHelper对象。应用程序在使用框架前必须注册实体类型,向实体类型注册列表添加将要操作的实体类型,应用程序注册实体列表时不会立即导致代码的自动生成和编译。
我们首先定义了一个基础的抽象类型RecordORMHelper,该类型定义了处理实体类型和数据库的映射操作,主要包括从一个System.Data.IDataReader读取数据并创建实体类型,为新增,修改和删除数据库记录而初始化System.Data.IDbCommand对象等等。该类型是快速ORM框架的核心处理对象,数据库处理模块将使用RecordORMHelper来作为统一的接口来处理实体类和数据库的映射操作。
代码生成器分析实体类型列表中所有没有处理的实体类型,获得其中的使用BindTableAttribute和BindFieldAttribute特性保存的对象和数据库的映射关系,针对每一个实体类型创建一个Class的代码,该Class是从RecordORMHelper上派生的,并实现了RecordORMHelper预留的接口。代码生成器可以同时为多个实体类型创建C#源代码,此时一份C#源代码中包含了多个从RecordORMHelper派生的Class类。
C#代码编译器接受代码生成器生成的代码,进行编译生成一个临时程序集,该程序集中就包含了多个派生自RecordORMHelper的类型,每一个类型都专门处理某种实体类型。编译器在编译程序是需要指定所引用的其他程序集,这里包括 mscorlib.dll,System.dll和System.Data.dll,此外还包括类型RecordORMHelper所在的程序集,也就是包括快速ORM框架的程序集,这里的程序集不一定是DLL格式,也可能是EXE格式。于是我们编译程序时引用了一个EXE,这种操作在使用VS.NET等开发工具时是禁止的。从这里可以看出,一些使用VS.NET开发工具所不可能实现的功能我们可以编程使用.NET框架来实现。
.NET框架自己包含了一个C#代码编译器,它的文件名是CSC.EXE,在.NET框架的安装目录下,在笔者的电脑中其路径是 C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v1.1.4322\csc.exe或者 C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\csc.exe,它是一个基于命令行的编辑器,能将C#代码编译生成EXE或者DLL文件。关于C#代码编译器可参考MSDN中的相关说明。
快速ORM框架的控制模块接受应用程序的请求,首先检查实体类型注册列表,若列表中没有找到相应的RecordORMHelper对象,则调用代码生成器生成代码,然后调用C#代码编译器编译生成临时的程序集,然后加载临时程序集,使用反射(调用System.Reflection.Assembly.GetType函数)找到其中所有的的RecordORMHelper类型,然后根据类型动态的创建对象实例,并填充到实体类型注册列表。最后调用RecordORMHelper预定的接口来实现ORM功能。
若我们在使用快速ORM框架前,将所有可能要用到的实体对象类型添加到实体类型注册列表中,则快速ORM框架会生成一个临时程序集,但我们是陆陆续续的往ORM框架注册实体对象类型,则快速ORM框架内部可能会多次调用代码生成器和代码编译器来生成临时程序集,这样最后会生成多个临时程序集。一般的建议在使用框架前将向ORM框架注册所有可能用到的实体对象类型,这样框架只会执行一次动态编译的操作。
基础类型RecordORMHelper
本类型属于ORM框架的底层模块。其代码为
:
public abstract class RecordORMHelper
{
///
<summary>/// 对象操作的数据表名称/// </summary>
public abstract string TableName
{
get ;
}
///
<summary>/// 从数据读取器读取数据创建一个记录对象/// </summary>
///数据读取器
///读取的数据
public object ReadRecord( System.Data.IDataReader reader )
{
int[] indexs = GetFieldIndexs( reader );
return InnerReadRecord( reader ,indexs );
}
///
<summary>/// 从数据读取器读取数据创建若干个记录对象/// </summary>
///数据读取器
///允许读取的最大的记录个数,为0则无限制
///读取的数据对象列表
public System.Collections.ArrayList ReadRecords( System.Data.IDataReader reader , int MaxRecordCount )
{
System.Collections.ArrayList list = new System.Collections.ArrayList();
int[] indexs = GetFieldIndexs( reader );
while( reader.Read())
{
object record = InnerReadRecord( reader , indexs );
list.Add( record );
if( MaxRecordCount > 0 && list.Count >= MaxRecordCount )
{
break;
}
}//while
return list ;
}
///
<summary>/// 从一个数据读取器中读取一条记录对象,必须重载/// </summary>
///数据读取器
///字段序号列表
///读取的记录对象
protected abstract object InnerReadRecord( System.Data.IDataReader reader , int[] FieldIndexs );
///
<summary>/// 为删除记录而初始化数据库命令对象/// </summary>
///数据库命令对象
///实体对象实例
///添加的SQL参数个数
public abstract int FillDeleteCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord );
///
<summary>/// 为插入记录而初始化数据库命令对象/// </summary>
///数据库命令对象
///实体对象实例
///添加的SQL参数个数
public abstract int FillInsertCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord );
///
<summary>/// 为更新数据库记录而初始化数据库命令对象/// </summary>
///数据库命令对象
///实体对象实例
///添加的SQL参数个数
public abstract int FillUpdateCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord );
///
<summary>/// 字段列表数组/// </summary>
protected abstract string[] RecordFieldNames
{
get ;
}
///
<summary>/// 针对特定的数据读取器获得实体对象的各个属性对应的数据栏目的编号/// </summary>
///数据读取器
///编号列表
private int[] GetFieldIndexs( System.Data.IDataReader reader )
{
if( reader == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("reader");
}
string[] FieldNames = this.RecordFieldNames ;
int[] indexs = new int[ FieldNames.Length ] ;
int FieldCount = reader.FieldCount ;
string[] names = new string[ FieldCount ] ;
for( int iCount = 0 ; iCount < FieldCount ; iCount ++ )
{
names[ iCount ] = reader.GetName( iCount ) ;
}
for( int iCount = 0 ; iCount < indexs.Length ; iCount ++ )
{
indexs[ iCount ] = -1 ;
string name = FieldNames[ iCount ] ;
for( int iCount2 = 0 ; iCount2 < FieldCount ; iCount2 ++ )
{
if( EqualsFieldName( name , names[ iCount2 ] ))
{
indexs[ iCount ] = iCount2 ;
break;
}
}
}
for( int iCount = 0 ; iCount < FieldCount ; iCount ++ )
{
string name = reader.GetName( iCount );
for( int iCount2 = 0 ; iCount2 < indexs.Length ; iCount2 ++ )
{
if( EqualsFieldName( name , FieldNames[ iCount2 ] ))
{
indexs[ iCount2 ] = iCount ;
}
}
}
return indexs ;
}
///
<summary>/// 连接多个字符串,各个字符串之间用逗号分隔,本函数会在动态生成的派生类中使用/// </summary>
///字符串集合
///连接所得的大字符串
protected string ConcatStrings( System.Collections.IEnumerable strs )
{
System.Text.StringBuilder myStr = new System.Text.StringBuilder();
foreach( string str in strs )
{
if( myStr.Length > 0 )
{
myStr.Append(",");
}
myStr.Append( str );
}//foreach
return myStr.ToString();
}
///
<summary>/// 判断两个字段名是否等价/// </summary>
///字段名1
///字段名2
///true:两个字段名等价 false:字段名不相同
private bool EqualsFieldName( string name1 , string name2 )
{
if( name1 == null || name2 == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("name1 or name2");
}
name1 = name1.Trim();
name2 = name2.Trim();
// 进行不区分大小写的比较
if( string.Compare( name1 , name2 , true ) == 0 )
{
return true ;
}
int index = name1.IndexOf(".");
if( index > 0 )
{
name1 = name1.Substring( index + 1 ).Trim();
}
index = name2.IndexOf(".");
if( index > 0 )
{
name2 = name2.Substring( index + 1 ).Trim();
}
return string.Compare( name1 , name2 , true ) == 0 ;
}
#region 从数据库读取的原始数据转换为指定数据类型的函数群,本函数会在动态生成的派生类中使用
protected byte ConvertToByte( object v , byte DefaultValue )
{
if( v == null || DBNull.Value.Equals( v ))
return DefaultValue ;
else
return Convert.ToByte( v );
}
protected sbyte ConvertToSByte( object v , sbyte DefaultValue )
{
if( v == null || DBNull.Value.Equals( v ))
return DefaultValue ;
else
return Convert.ToSByte( v );
}
其他的 ConvertTo 函数
#endregion
///
<summary>/// 将日期数据转换为数据库中的格式,本函数会在动态生成的派生类中使用./// </summary>
///日期数据
///保存格式化字符串
///转换后的数据
protected object DateTimeToDBValue( DateTime Value , string Format )
{
if( Format != null || Format.Length > 0 )
{
return Value.ToString( Format );
}
else
{
return Value ;
}
}
}//public abstract class RecordORMHelper
在这个类型中,TableName属性返回该实体对象类型绑定的数据库名称,因此该属性值由BindTableAttribute特性指定,RecordFieldNames属性返回一个字符串数组,该数组列出了所有的绑定的字段的名称,也就是实体类型包含的所有的BindFieldAttribute指定的字段名称组成的数组。
实体类型注册列表
在快速ORM框架主模块MyFastORMFramework中定义了一个myRecordHelpers的变量
|
private static System.Collections.Hashtable myRecordHelpers = new System.Collections.Hashtable();
|
这个myRecordHelpers就是实体类型注册列表。该列表中键值就是实体对象类型,而它的数据值就是一个个动态生成的从RecordORMHelper派生的对象实例。我们定义了一个函数向该列表注册实体对象类型
public void RegisterType( Type t )
{
if( myRecordHelpers.ContainsKey( t ) == false )
{
this.GetBindProperties( t );
myRecordHelpers[ t ] = null ;
}
}
这个过程很简单,就是向该列表的键值列表添加实体对象类型,这里调用了GetBindProperties函数,该函数内部会仔细检查实体对象类型是否符合快速ORM框架的要求,若不符合则会报错,因此这里调用GetBindProperties函数就是检查实体对象类型是否合格。
ORM框架操作数据库前都会查询实体类型注册列表获得所需的数据库操作帮助器,也就是调用函数GetHelepr,其代码为:
private RecordORMHelper GetHelper( Type RecordType )
{
RecordORMHelper helper = null ;
if( myRecordHelpers.ContainsKey( RecordType ))
{
helper = ( RecordORMHelper ) myRecordHelpers[ RecordType ] ;
if( helper != null )
{
return helper ;
}
}
else
{
this.GetBindProperties( RecordType );
myRecordHelpers[ RecordType ] = null;
}
BuildHelpers( null );
helper = ( RecordORMHelper ) myRecordHelpers[ RecordType ] ;
if( helper == null )
{
throw new ArgumentException("为类型 " + RecordType.FullName + " 初始化系统错误");
}
return helper ;
}
在这个函数中,参数就是实体对象类型,首先从注册列表中获得数据库操作帮助器,若没有找到则进行注册,然后调用BuildHelpers执行动态编译生成数据库操作帮助器。然后再尝试从注册列表中获得数据库操作帮助器。
在ORM框架中,GetHelper函数会频繁的调用,因此使用实体对象类型注册列表可以提高系统性能。应用系统多次连续的调用RegisterType函数会导致类型注册列表中有多个类型对应的数据库操作帮助器是空的,而再BuildHelpers函数内部会对所有的没有设定数据库操作帮助器的实体对象类型执行动态编译的操作,能一下子生成多个数据库操作帮助器,这样能尽量减少动态编译的次数。
代码生成器
在动态编译框架中,代码生成器是非常重要的部分。没有代码生成器,动态编译框架成了无源之水,无米之炊了。代码生成器的主要工作就是使用反射解析数据库实体类的结构,分析其中的数据库绑定信息,然后使用字符串拼凑的操作来生成C#代码字符串。
要设计出代码生成器,首先的设计出其要输出的C#代码的结构,我们可以不使用那个基础的RecordORMHelper而完全依赖生成的C#代码来完成数据库的映射功能,不过即使用代码生成器,我们也得考虑到代码的重用,于是我们把一些通用的代码放到RecordORMHelper中,然后动态生成的C#类就继承自RecordORMHelper。
ORM框架中还包含了一个IndentTextWriter的支持缩进的文本书写器,虽然我们可以完全使用字符串加号操作来生成代码文本,但使用IndentTextWriter能让工作更高效,生成的代码也便于人们阅读,这有利于代码生成器的调试和维护。在IndentTextWriter中,使用BeginGroup来开始缩进一段代码块,使用EndGroup来结束缩进一段代码块,使用WriteLine来输出一行代码文本。
在快速ORM框架中,代码生成器包含在函数MyFastORMFramework.GenerateCode中。现对其过程进行说明
启用命名参数
在MyFastORMFramework中定义了NamedParameter属性用于决定是否启动命名参数。为了安全,代码生成器生成的SQL命令文本不会包含具体的数值,而是使用SQL命令参数的方式。若设置该属性,则启用命名参数,此时代码生成器生成SQL文本中使用“@参数名”来表示SQL命令参数占位,若没有设置该属性,则未启用命名参数,此时代码生成器生成的SQL文本中使用“?”来表示SQL命令参数占位。比如对于新增记录,若启用命令参数,则生成的SQL文本为“Insert Into Table ( Field1 , Field2 ) Values ( @Value1 , @Value2 )”,若不启用命名参数则生成的SQL文本为“Insert Into Table( Field1 , Field2 ) Values( ? , ? )”。
某些类型的数据库不支持无命名的参数,有些支持,因此本快速ORM框架提供了NamedParamter属性方法让使用者进行调整,使得快速ORM框架能适用于更多类型的数据库。
生成读取数据的代码
基础类型RecordORMHelper中函数 ReadRecord调用GetFieldIndexs和InnerReadRecord函数从一个IDataReader中读取一行数据并创建一个实体类型的实例。GetFieldIndexs 函数用于获得一个整数数组,该数组的元素就是实体类各个属性对应的数据读取器的从0开始计算的字段栏目序号。例如对于属性 DB_Employees. EmployeeID,它是对象的第一个属性成员,其绑定的字段是“EmployeeID”。若数据读取器的第三个栏目,也就是对它调用IDataReader.GetName( 3 )的值是“employeeid”,则GetFieldIndexs函数返回的数组第一个元素值就是3。若数据读取器没有找到和“EmployeeID”相匹配的栏目,则GetFieldIndexs函数返回的数组的第一个元素值是-1。使用GetFieldIndexs的返回值,ORM框架可以使用比较快速的IDataReader.GetValue( index )来读取数据而不必使用慢速的 IDataReader.GetValue( name )了。
InnerReadRecord需要代码生成器来生成代码进行扩展,对于DB_Employees,其扩展的代码为
protected override object InnerReadRecord( System.Data.IDataReader reader , int[] FieldIndexs )
{
MyORM.DB_Employees record = new MyORM.DB_Employees();
int index = 0 ;
index = FieldIndexs[ 0 ]; // 读取字段 EmployeeID
if( index >= 0 )
{
record.EmployeeID = ConvertToInt32( reader.GetValue( index ) , ( int ) 0) ;
}
index = FieldIndexs[ 1 ]; // 读取字段 LastName
if( index >= 0 )
{
record.LastName = ConvertToString( reader.GetValue( index ) , null ) ;
}
读取其他字段值……
return record ;
}
在这段自动生成的代码中,参数reader就是类型为IDataReader的数据读取器,而FieldIndexs就是GetFieldIndexs的返回值。在InnerReadRecord函数中会一次读取FieldIndexs的元素值,根据属性的数据类型而调用ConvertToInt32,ConvertToString等一系列的ConvertTo函数,而这一系列的函数已经在基础类型RecordORMHelper中定义好了。
从这个自动生成的代码可以看出,ORM框架使用实体类的属性,GetFieldIndexs和数据读取器实现了如下的映射过程
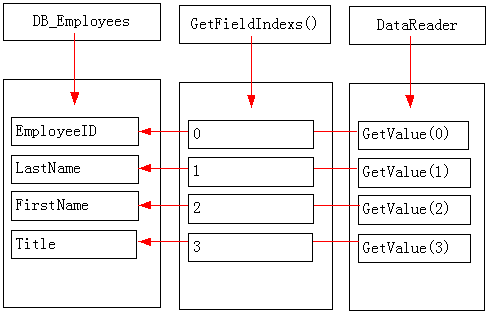
在这个过程中,GetFieldIndexs函数提供了一个映射表,而自动生成的代码就是利用这个映射表将数据从DataReader复制到DB_Employees的属性中。
我们自动生成代码实现了InnerReadRecord函数后,在ORM框架中就可以调用基础的RecordORMHelper中的ReadRecord函数读取一行数据并生成一个实体对象,而函数ReadRecords是ReadRecord的另外一个读取多个数据的版本。
根据上述设计,我们可以使用以下代码来生成InnerReadRecord代码
myWriter.WriteLine("// 从数据读取器读取数据创建对象");
myWriter.WriteLine("protected override object InnerReadRecord( System.Data.IDataReader reader , int[] FieldIndexs )");
myWriter.BeginGroup("{");
myWriter.WriteLine( RecordType.FullName + " record = new " + RecordType.FullName + "();");
myWriter.WriteLine("int index = 0 ;");
// 获得类型中绑定到数据库的属性信息
for( int iCount = 0 ; iCount < ps.Length ; iCount ++ ) { System.Reflection.PropertyInfo p = ps[ iCount ] ; if( p.CanWrite == false ) { continue ; } BindFieldAttribute fa = ( BindFieldAttribute ) Attribute.GetCustomAttribute( p , typeof( BindFieldAttribute )); myWriter.WriteLine(""); myWriter.WriteLine("index = FieldIndexs[ " + iCount + " ]; // 读取字段 " + GetBindFieldName( p )); myWriter.WriteLine("if( index >= 0 )");
myWriter.BeginGroup("{");
Type pt = p.PropertyType ;
object DefaultValue = this.GetDefaultValue( p );
string strRead = null;
if( pt.Equals( typeof( byte )))
{
strRead = "ConvertToByte( reader.GetValue( index ) , " + GetValueString( pt , DefaultValue ) + ")";
}
else if( pt.Equals( typeof( sbyte )))
{
strRead = "ConvertToSByte( reader.GetValue( index ) , " + GetValueString( pt , DefaultValue ) + ")";
}
else if( pt.Equals( typeof( short )))
{
strRead = "ConvertToInt16( reader.GetValue( index ) , " + GetValueString( pt , DefaultValue ) + ")";
}
处理其他数据类型……
else if( pt.Equals( typeof( DateTime )))
{
string strDefault = "DateTime.MinValue" ;
DateTime dt = Convert.ToDateTime( DefaultValue );
if( dt.Equals( DateTime.MinValue ) == false )
{
strDefault = "new DateTime( " + dt.Ticks + ")";
}
strRead = "ConvertToDateTime( reader.GetValue( index ) , " + strDefault + " , " + ( fa.ReadFormat == null ? "null" : "\"" + fa.ReadFormat + "\"" ) + " )";
}
else if( pt.Equals( typeof( string )))
{
strRead = "ConvertToString( reader.GetValue( index ) , " + ( DefaultValue == null ? "null" : "@\"" + DefaultValue.ToString() + "\"" ) + " )";
}
else if( pt.Equals( typeof( char )))
{
strRead = "ConvertToChar( reader.GetValue( index ) , " + GetValueString( pt , DefaultValue ) + " )";
}
else
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("不支持属性类型" + p.Name + " " + pt.FullName );
}
myWriter.WriteLine("record." + p.Name + " = " + strRead + " ;" );
myWriter.EndGroup("}");
}//for
myWriter.WriteLine("");
myWriter.WriteLine("return record ;");
myWriter.EndGroup(")//InnerReadRecord");
在这段代码中,ps是一个事先分析了DB_Employees结构而得出的System.Rection.PropertyInfo数组,包含了所有附加了BindFieldAttribute的成员属性,它是调用GetBindProperties函数获得的返回值。GetDefaultValue用于获得针对某个属性的默认值,若调用reader.GetValue( index )获得了一个空值,也就是DBNull.Value则设置属性为默认值;GetValueString是将一个数值转换为C#代码的表达样式。然后针对不同的属性数据类型生成对应的ConvertTo代码。
函数GetBindProperties的代码为
private System.Reflection.PropertyInfo[] GetBindProperties( Type RecordType )
{
if( RecordType == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("ReocrdType");
}
if( RecordType.IsPublic == false )
{
throw new ArgumentException("类型 " + RecordType.FullName + " 不是公开类型");
}
if( RecordType.IsClass == false )
{
throw new ArgumentException("类型 " + RecordType.FullName + " 不是类");
}
if( RecordType.IsAbstract )
{
throw new ArgumentException("类型 " + RecordType.FullName + " 不得是抽象类");
}
// 检查是否有可用的无参数的构造函数
// 也就是判断语句 Record obj = new Record() 是否有效
if( RecordType.GetConstructor( new Type[]{}) == null )
{
throw new ArgumentException("类型 " + RecordType.FullName + " 没有默认构造函数" );
}
System.Collections.ArrayList properties = new System.Collections.ArrayList();
System.Reflection.PropertyInfo[] ps = RecordType.GetProperties(
System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Instance
| System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Public );
foreach( System.Reflection.PropertyInfo p in ps )
{
BindFieldAttribute fa = ( BindFieldAttribute ) Attribute.GetCustomAttribute(
p , typeof( BindFieldAttribute ));
if( fa != null )
{
System.Reflection.ParameterInfo[] pps = p.GetIndexParameters();
if( pps != null && pps.Length > 0 )
{
throw new ArgumentException("属性 " + RecordType.FullName + "." + p.Name + " 不得有参数");
}
Type pt = p.PropertyType ;
if( pt.IsPrimitive || pt.Equals( typeof( string )) || pt.Equals( typeof( DateTime )))
{
}
else
{
throw new ArgumentException("不支持属性 " + RecordType.FullName + "." + p.Name + " 的数据类型 " + pt.FullName );
}
properties.Add( p );
}
}
if( properties.Count == 0 )
{
throw new ArgumentException("类型 " + RecordType.FullName + " 没有标记为绑定到任何字段");
}
return ( System.Reflection.PropertyInfo[] ) properties.ToArray( typeof( System.Reflection.PropertyInfo ));
}
从这个函数可以看出,快速ORM框架处理的实体类型必须是一个类型,必须公开,不得是抽象的,而且有公开的无参数的构造函数。这里使用了.NET框架的反射技术,首先使用Type.GetConstructor函数获得对象类型指定样式的构造函数对象,还使用GetProperties函数获得实体类型的所有的公开实例属性。若属性附加了BindFieldAttribute特性则添加到输出列表中。注意,属性的数据类型必须是CLR基础数据类型,字符串或者时间日期格式,其他的数据类型是不合要求的。
这里还调用了一个GetBindFieldName获得属性绑定的数据库字段名,其代码为
private string GetBindFieldName( System.Reflection.PropertyInfo p )
{
BindFieldAttribute fa = ( BindFieldAttribute ) Attribute.GetCustomAttribute(
p , typeof( BindFieldAttribute ));
string name = fa.Name ;
if( name != null )
name = name.Trim();
if( name == null || name.Length == 0 )
name = p.Name ;
return name ;
}
其功能很简单,就是检查属性是否附加了BindFieldAttribute特性,若附加了则使用该特性的Name值,若没有则直接返回属性的名称。
生成插入数据的代码
基础类型RecordORMHelper预留了FillInsertCommand函数,该函数就是为插入数据库记录而设置数据库命令对象(IDbCommand)的。对于DB_Employees,其代码为
public override int FillInsertCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord )
{
if( cmd == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException("cmd");
if( objRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException("objRecord");
MyORM.DB_Employees myRecord = objRecord as MyORM.DB_Employees ;
if( myRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentException("must type 'MyORM.DB_Employees' ");
System.Collections.ArrayList myFieldNames = new System.Collections.ArrayList();
System.Collections.ArrayList myValues = new System.Collections.ArrayList();
myFieldNames.Add( "EmployeeID" );
myValues.Add( myRecord.EmployeeID );
if( myRecord.LastName != null )
{
myFieldNames.Add( "LastName" );
myValues.Add( myRecord.LastName );
}
myFieldNames.Add( "BirthDate" );
myValues.Add( myRecord.BirthDate.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd") );
处理其他属性值……
myFieldNames.Add( "Sex" );
myValues.Add( myRecord.Sex );
if( myFieldNames.Count == 0 ) return 0 ;
cmd.Parameters.Clear() ;
System.Text.StringBuilder mySQL = new System.Text.StringBuilder();
mySQL.Append( "Insert Into Employees ( " );
mySQL.Append( ConcatStrings( myFieldNames ));
mySQL.Append( " ) Values ( " );
for( int iCount = 0 ; iCount < myValues.Count ; iCount ++ ) { if( iCount > 0 ) mySQL.Append(" , " );
mySQL.Append(" ? ") ;
System.Data.IDbDataParameter parameter = cmd.CreateParameter();
parameter.Value = myValues[ iCount ] ;
cmd.Parameters.Add( parameter );
}//for
mySQL.Append( " ) " );
cmd.CommandText = mySQL.ToString();
return myValues.Count ;
}
在这段代码中,首先是检查参数是否正确。然后处理实体类型的所有的属性。若属性值等于默认值则跳过处理,否则将属性绑定的字段的名称保存到myFieldNames列表中,属性值保存到myValues列表中。最后使用字符串拼凑的操作来生成SQL命令文本,若NamedParameter属性为Ture,则生成的SQL文本为“Insert Into TableName ( FieldName1 , FieldName2 … ) Values ( @Value1 , @Value2 …)”,若该属性为False,则生成的SQL文本为“Insert Into TableName ( FieldName1 , FieldName2 … ) Values ( ? , ? …)”,并将属性值添加到数据库命令对象的参数列表中,该函数返回保存数据的属性的个数。
对于字符串类型的属性,其默认值就是“DBNull”。而对于其他的整数或者日期类型的属性,并没有默认值,因此是无条件的插入到数据库中。
我们使用以下的代码来生成上述代码文本
myWriter.WriteLine("public override int FillInsertCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord )");
myWriter.BeginGroup("{");
myWriter.WriteLine("if( cmd == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(\"cmd\");");
myWriter.WriteLine("if( objRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(\"objRecord\");");
myWriter.WriteLine(RecordType.FullName + " myRecord = objRecord as " + RecordType.FullName + " ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("if( myRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentException(\"must type '" + RecordType.FullName + "' \");");
myWriter.WriteLine("System.Collections.ArrayList myFieldNames = new System.Collections.ArrayList();");
myWriter.WriteLine("System.Collections.ArrayList myValues = new System.Collections.ArrayList();");
for (int iCount = 0; iCount < ps.Length; iCount++) { System.Reflection.PropertyInfo p = ps[iCount]; if (p.CanRead == false) { continue; } BindFieldAttribute fa = (BindFieldAttribute)Attribute.GetCustomAttribute( p, typeof(BindFieldAttribute)); string FieldName = GetBindFieldName(p); myWriter.WriteLine(""); Type pt = p.PropertyType; object DefaultValue = this.GetDefaultValue(p); if (pt.Equals(typeof(string))) { myWriter.WriteLine("if( myRecord." + p.Name + " != null && myRecord." + p.Name + ".Length != 0 )"); myWriter.BeginGroup("{"); myWriter.WriteLine("myFieldNames.Add( \"" + FieldName + "\" );"); myWriter.WriteLine("myValues.Add( myRecord." + p.Name + " );"); myWriter.EndGroup("}"); } else if (pt.Equals(typeof(DateTime))) { myWriter.WriteLine("myFieldNames.Add( \"" + FieldName + "\" );"); if (fa.WriteFormat != null && fa.WriteFormat.Length > 0)
{
myWriter.WriteLine("myValues.Add( myRecord." + p.Name + ".ToString(\"" + fa.WriteFormat + "\") );");
}
else
{
myWriter.WriteLine("myValues.Add( myRecord." + p.Name + ".ToString(\"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss\") );");
}
}
else
{
myWriter.WriteLine("myFieldNames.Add( \"" + FieldName + "\" );");
myWriter.WriteLine("myValues.Add( myRecord." + p.Name + " );");
}
}//for
myWriter.WriteLine("");
myWriter.WriteLine("if( myFieldNames.Count == 0 ) return 0 ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("cmd.Parameters.Clear() ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("System.Text.StringBuilder mySQL = new System.Text.StringBuilder();");
myWriter.WriteLine("mySQL.Append( \"Insert Into " + TableName + " ( \" );");
myWriter.WriteLine("mySQL.Append( ConcatStrings( myFieldNames ));");
myWriter.WriteLine("mySQL.Append( \" ) Values ( \" );");
myWriter.WriteLine("for( int iCount = 0 ; iCount < myValues.Count ; iCount ++ )"); myWriter.BeginGroup("{"); myWriter.WriteLine("if( iCount > 0 ) mySQL.Append(\" , \" );");
if (bolNamedParameter)
{
myWriter.WriteLine("mySQL.Append(\" @Value\" + iCount ) ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("System.Data.IDbDataParameter parameter = cmd.CreateParameter();");
myWriter.WriteLine("parameter.Value = myValues[ iCount ] ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("parameter.ParameterName = \"Value\" + iCount ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("cmd.Parameters.Add( parameter );");
}
else
{
myWriter.WriteLine("mySQL.Append(\" ? \") ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("System.Data.IDbDataParameter parameter = cmd.CreateParameter();");
myWriter.WriteLine("parameter.Value = myValues[ iCount ] ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("cmd.Parameters.Add( parameter );");
}
myWriter.EndGroup("}//for");
myWriter.WriteLine("mySQL.Append( \" ) \" );");
myWriter.WriteLine("cmd.CommandText = mySQL.ToString();");
myWriter.WriteLine("return myValues.Count ;");
myWriter.EndGroup(")//public override int FillInsertCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord )");
在这里我们首先输出检查参数的代码文本,然后遍历所有绑定字段的属性对象,根据属性的数据类型分为字符串样式,日期样式和其他样式。对于字符串样式则需要输出判断是否为空的代码,对于日期样式则还要考虑BindFieldAttribute特性中指明的数据保存样式,对于其他样式则没有任何判断,直接输出。
生成删除数据的代码
基础类型RecordORMHelper预留了FillDeleteCommand函数,代码生成器自动生成代码来实现FillDeleteCommand函数,而ORM框架就会创建一个数据库命令对象,然后调用FillDeleteCommand函数来为删除数据而初始化数据库命令对象,然后执行SQL命令删除数据。
在DB_Employees中使用一下代码来定义EmployeeID属性的。
///
<summary>/// 字段值 EmployeeID/// </summary>
private System.Int32 m_EmployeeID = 0 ;
///
<summary>/// 字段值 EmployeeID/// </summary>
[BindField("EmployeeID" , Key = true )]
public System.Int32 EmployeeID
{
get
{
return m_EmployeeID ;
}
set
{
m_EmployeeID = value;
}
}
附加的BindField特性中使用了“Key=true”指明了EmployeeID字段是关键字段。于是我们很容易就想到使用SQL语句“Delete From Employees Where EmployeeID=指定的员工编号”来删除数据。于是针对DB_Employees代码生成器生成的代码如下
public override int FillDeleteCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord )
{
if( cmd == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException("cmd");
if( objRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException("objRecord");
MyORM.DB_Employees myRecord = objRecord as MyORM.DB_Employees ;
if( myRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentException("must type 'MyORM.DB_Employees' ");
cmd.Parameters.Clear();
cmd.CommandText = @"Delete From Employees Where EmployeeID = ? " ;
System.Data.IDbDataParameter parameter = null ;
parameter = cmd.CreateParameter();
parameter.Value = myRecord.EmployeeID ;
cmd.Parameters.Add( parameter );
return 1 ;
}
我们可以使用以下代码来生成上述的C#代码文本。
// 关键字段SQL参数名称列表
System.Collections.ArrayList KeyParameterNames = new System.Collections.ArrayList();
// 生成Where子语句文本
System.Text.StringBuilder myWhereSQL = new System.Text.StringBuilder();
System.Collections.ArrayList KeyProperties = new System.Collections.ArrayList();
for (int iCount = 0; iCount < ps.Length; iCount++) { System.Reflection.PropertyInfo p = ps[iCount]; if (p.CanRead == false) { continue; } BindFieldAttribute fa = (BindFieldAttribute)Attribute.GetCustomAttribute( p, typeof(BindFieldAttribute)); if (fa.Key == false) { continue; } string FieldName = this.GetBindFieldName(p); if (myWhereSQL.Length > 0)
{
myWhereSQL.Append(" and ");
}
KeyProperties.Add(p);
if (bolNamedParameter)
{
string pName = "Key" + p.Name;
KeyParameterNames.Add(pName);
myWhereSQL.Append(FixFieldName(FieldName) + " = @" + pName + " ");
}
else
{
myWhereSQL.Append(FixFieldName(FieldName) + " = ? ");
}
}//for
myWriter.WriteLine("public override int FillDeleteCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord )");
myWriter.BeginGroup("{");
if (KeyProperties.Count == 0)
{
myWriter.WriteLine("throw new NotSupportedException(\"FillDeleteCommand\");");
}
else
{
myWriter.WriteLine("if( cmd == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(\"cmd\");");
myWriter.WriteLine("if( objRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(\"objRecord\");");
myWriter.WriteLine(RecordType.FullName + " myRecord = objRecord as " + RecordType.FullName + " ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("if( myRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentException(\"must type '" + RecordType.FullName + "' \");");
System.Text.StringBuilder myDeleteSQL = new System.Text.StringBuilder();
myDeleteSQL.Insert(0, "Delete From " + TableName + " Where " + myWhereSQL.ToString());
myWriter.WriteLine("cmd.Parameters.Clear();");
myWriter.WriteLine("cmd.CommandText = @\"" + myDeleteSQL.ToString() + "\" ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("System.Data.IDbDataParameter parameter = null ;");
int index = 0;
foreach (System.Reflection.PropertyInfo p in KeyProperties)
{
myWriter.WriteLine("");
myWriter.WriteLine("parameter = cmd.CreateParameter();");
WriteSetParameterValue(p, myWriter);
if (bolNamedParameter)
{
myWriter.WriteLine("parameter.ParameterName = \"" + KeyParameterNames[index] + "\";");
}
myWriter.WriteLine("cmd.Parameters.Add( parameter );");
index++;
}
myWriter.WriteLine("");
myWriter.WriteLine("return " + KeyProperties.Count + " ;");
}
myWriter.EndGroup(")");
myWriter.EndGroup(“)”);
在这段代码中,首先是遍历实体类型中所有的绑定到字段的属性,根据其附加的BindFieldAttribute特性的Key值找到所有的关键字段属性对象,并创建了一个“关键字段名1=@Key属性名1 And 关键字段名2=@Key属性名2”(若未启用命名参数则为“关键字段名1=? And 关键字段名2=? ……”)格式的字符串,该字符串就是SQL语句的Where子语句了,若启用命名参数则生成的文本为。
若没有找到任何关键属性,则无法确定删除记录使用的查询条件,此时代码生成器就会输出抛出异常的代码。在这里代码生成器不会直接抛出异常而导致ORM框架过早的报警,未来可能有开发人员定义的实体类型只是为了查询或者新增数据库记录,那时不需要定义关键属性。若对这种实体类型过早的报警则减少了快速ORM框架的使用范围。
若实体类型定义了一个或者多个关键属性,则开始输出代码文本,首先输出检查参数的代码文本,然后遍历所有的关键属性对象,生成向数据库命令对象添加参数的代码。
这里还用到了一个WriteSetParamterValue的方法用于书写设置参数值的过程,其代码为
private void WriteSetParameterValue( System.Reflection.PropertyInfo p , IndentTextWriter myWriter )
{
if (p.PropertyType.Equals(typeof(DateTime)))
{
BindFieldAttribute fa = (BindFieldAttribute)Attribute.GetCustomAttribute(
p, typeof(BindFieldAttribute));
if (fa.WriteFormat == null || fa.WriteFormat.Length == 0)
{
myWriter.WriteLine("parameter.Value = myRecord." + p.Name + ".ToString(\"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss\");");
}
else
{
myWriter.WriteLine("parameter.Value = myRecord." + p.Name + ".ToString(\"" + fa.WriteFormat + "\");");
}
}
else if (p.PropertyType.Equals(typeof(string)))
{
myWriter.WriteLine("if( myRecord." + p.Name + " == null || myRecord." + p.Name + ".Length == 0 )");
myWriter.WriteLine(" parameter.Value = System.DBNull.Value ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("else");
myWriter.WriteLine(" parameter.Value = myRecord." + p.Name + " ;");
}
else
{
myWriter.WriteLine("parameter.Value = myRecord." + p.Name + " ;");
}
}
该方法内判断若属性数据类型为时间型则设置输出的数据格式,若为字符串类型,则判断数据是否为空,若为空则设置参数值为DBNull。
生成更新数据的代码
基础类型RecordORMHelper预留了FillUpdateCommand函数,快速ORM框架更新数据库时首先创建一个数据库命令对象,然后调用FillUpdateCommand函数设置SQL语句,添加SQL参数,然后执行该命令对象接口更新数据库记录。对于DB_Employees,其FillUpdateCommand函数的代码为
public override int FillUpdateCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord )
{
if( cmd == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException("cmd");
if( objRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException("objRecord");
MyORM.DB_Employees myRecord = objRecord as MyORM.DB_Employees ;
if( myRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentException("must type 'MyORM.DB_Employees' ");
cmd.CommandText = @"Update Employees Set EmployeeID = ? , LastName = ? , FirstName = ? , Title = ? , TitleOfCourtesy = ? , Address = ? , BirthDate = ? , City = ? , Country = ? , EducationalLevel = ? , EMail = ? , Extension = ? , Goal = ? , HireDate = ? , HomePage = ? , HomePhone = ? , Notes = ? , PostalCode = ? , Region = ? , ReportsTo = ? , Sex = ? Where EmployeeID = ? " ;
cmd.Parameters.Clear();
System.Data.IDbDataParameter parameter = null ;
parameter = cmd.CreateParameter();
parameter.Value = myRecord.EmployeeID ;
cmd.Parameters.Add( parameter );
parameter = cmd.CreateParameter();
parameter.Value = myRecord.BirthDate.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd");
cmd.Parameters.Add( parameter );
为其他属性值添加SQL参数对象。。。。。。
parameter = cmd.CreateParameter();
parameter.Value = myRecord.Sex ;
cmd.Parameters.Add( parameter );
//这里为查询条件添加参数
parameter = cmd.CreateParameter();
parameter.Value = myRecord.EmployeeID ;
cmd.Parameters.Add( parameter );
return 22 ;
}
这段代码结构比较简单,首先是对参数进行判断,然后设置SQL更新语句,然后将所有的属性的值依次添加到SQL参数列表中,最后还为查询将EmployeeID值添加到SQL参数列表中。
在代码生成器中生成FillUpdateCommand代码文本的代码为
myWriter.WriteLine("public override int FillUpdateCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord )");
myWriter.BeginGroup("{");
if (KeyProperties.Count == 0)
{
myWriter.WriteLine("throw new NotSupportedException(\"FillUpdateCommand\");");
}
else
{
myWriter.WriteLine("if( cmd == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(\"cmd\");");
myWriter.WriteLine("if( objRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(\"objRecord\");");
myWriter.WriteLine(RecordType.FullName + " myRecord = objRecord as " + RecordType.FullName + " ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("if( myRecord == null ) throw new ArgumentException(\"must type '" + RecordType.FullName + "' \");");
// 更新用SQL语句文本
System.Text.StringBuilder myUpdateSQL = new System.Text.StringBuilder();
// 所有的SQL参数名称
System.Collections.ArrayList ParameterNames = new System.Collections.ArrayList();
foreach (System.Reflection.PropertyInfo p in ps)
{
if (p.CanRead == false)
{
continue;
}
string FieldName = this.GetBindFieldName(p);
if (myUpdateSQL.Length > 0)
{
myUpdateSQL.Append(" , ");
}
if (bolNamedParameter)
{
string pName = "Value" + p.Name;
ParameterNames.Add( pName );
myUpdateSQL.Append(FixFieldName(FieldName) + " = @" + pName);
}
else
{
myUpdateSQL.Append(FixFieldName(FieldName) + " = ? ");
}
}//foreach
ParameterNames.AddRange(KeyParameterNames);
myUpdateSQL.Insert(0, "Update " + FixTableName(TableName) + " Set ");
myUpdateSQL.Append(" Where " + myWhereSQL.ToString());
myWriter.WriteLine("");
myWriter.WriteLine("cmd.CommandText = @\"" + myUpdateSQL.ToString() + "\" ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("cmd.Parameters.Clear();");
myWriter.WriteLine("System.Data.IDbDataParameter parameter = null ;");
myWriter.WriteLine("");
System.Collections.ArrayList ps2 = new System.Collections.ArrayList();
ps2.AddRange(ps);
ps2.AddRange(KeyProperties);
foreach (System.Reflection.PropertyInfo p in ps2)
{
if (p.CanRead == false)
{
continue;
}
myWriter.WriteLine("");
myWriter.WriteLine("parameter = cmd.CreateParameter();");
WriteSetParameterValue(p, myWriter);
if (bolNamedParameter)
{
// 设置SQL命令对象的名称
myWriter.WriteLine("parameter.ParameterName = \"" + ParameterNames[0] + "\";");
ParameterNames.RemoveAt(0);
}
myWriter.WriteLine("cmd.Parameters.Add( parameter );");
}//foreach
myWriter.WriteLine("");
myWriter.WriteLine("return " + ps2.Count + " ;");
}//else
myWriter.EndGroup(")//public override int FillUpdateCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord )");
myWriter.EndGroup(“)//public override int FillUpdateCommand( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd , object objRecord )”);
这里的KeyProperties,KeyParameterNames和myWhereSQL的值都在生成FillDeleteCommand时已经设置好了,这里直接拿来用。若KeyProperties没有内容,说明实体类型没有指明绑定了关键字段的属性,此时无法生成更新时的查询语句,于是输出抛出异常的C#代码文本。
我们首先遍历实体类型中所有的绑定了字段的属性对象,拼凑出“Update TableName Set 字段名1=@Value属性名1 , 字段名2=@Value属性名2”(若未启用命名参数则输出为“Update TableName Set 字段名1=? , 字段名2=?”)样式的SQL文本,然后加上myWhereSQL中的查询条件文本,从而得出了完整的SQL语句,然后将其输出到代码文本中。
我们有一次遍历实体类型所有绑定了字段的属性对象,对于每一个属性输出添加SQL参数对象的C#代码文本。此外还遍历KeyProperties来生成添加查询条件SQL参数的C#代码文本。
函数最后返回添加的SQL参数个数的返回语句。
生成完整的C#源代码文本
在实现了生成读取数据,插入数据,删除数据和更新数据的代码文本的程序代码后,我们就可以实现完整的生成C#代码文本的程序代码了,这些程序代码就是方法GenerateCode的全部内容,其代码为
private string GenerateCode( string nsName , string strFileName , System.Collections.ArrayList RecordTypes )
{
// 开始创建代码
IndentTextWriter myWriter = new IndentTextWriter();
myWriter.WriteLine("using System;");
myWriter.WriteLine("using System.Data;");
myWriter.WriteLine("namespace " + nsName);
myWriter.BeginGroup("{");
// 对每一个数据容器对象创建数据处理类的代码
foreach (Type RecordType in RecordTypes)
{
string TableName = RecordType.Name;
BindTableAttribute ta = (BindTableAttribute)Attribute.GetCustomAttribute(
RecordType, typeof(BindTableAttribute), false);
if (ta != null)
{
TableName = ta.Name;
}
if (TableName == null || TableName.Trim().Length == 0)
{
TableName = RecordType.Name;
}
TableName = TableName.Trim();
System.Reflection.PropertyInfo[] ps = this.GetBindProperties(RecordType);
myWriter.WriteLine("public class " + RecordType.Name + "ORMHelper : " + typeof(RecordORMHelper).FullName);
myWriter.BeginGroup("{");
myWriter.WriteLine("");
myWriter.WriteLine("///
<summary>创建对象</summary>
");
myWriter.WriteLine("public " + RecordType.Name + "ORMHelper(){}");
myWriter.WriteLine("");
生成重载TableName的代码
生成重载RecordFieldNames的代码
生成重载FillUpdateCommand的代码
生成重载FillDeleteCommand的代码
生成重载FillInsertCommand的代码
生成重载InnerReadRecord的代码
}//foreach
myWriter.EndGroup("}//namespace");
// 若需要保存临时生成的C#代码到指定的文件
if (strFileName != null && strFileName.Length > 0)
{
myWriter.WriteFile(strFileName, System.Text.Encoding.GetEncoding(936));
}
return myWriter.ToString();
}
这个函数的参数是生成的代码的名称空间的名称,保存代码文本的文件名和要处理的数据库实体对象类型列表。在函数中首先创建一个myWriter的代码文本书写器,输出导入名称空间的代码文本,输出命名空间的代码文本,然后遍历RecordTypes列表中的所有的实体对象类型,对每一个实体对象类型输出一个定义类的C#代码文本,类名就是 类型名称+ORMHelper,该类继承自RecordORMHelper类型。然后执行上述的生成TableName,RecordFieldNames,FillUpdateCommand,FillDelteCommand,FillInsertCommand和InnerReadRecord的C#代码文本的过程,这样就完成了针对一个实体对象类型的C#代码的生成过程。
当代码生成器完成工作后,内置的代码文本书写器myWriter中就包含了完整的C#代码文本。这个代码文本中包含了多个从RecordORMHelper类型派生的数据库操作帮助类型。这样我们就可以随即展开动态编译的操作了。
动态编译
在代码生成器成功的生成所有的C#源代码文本后,我们就可以执行动态编译了,函数MyFastORMFramework.BuildHelpers就是实现动态编译,其代码为
private int BuildHelpers( string strFileName )
{
System.Collections.ArrayList RecordTypes = new System.Collections.ArrayList();
foreach( Type RecordType in myRecordHelpers.Keys )
{
if( myRecordHelpers[ RecordType ] == null )
{
RecordTypes.Add( RecordType );
}
}//foreach
if( RecordTypes.Count == 0 )
return 0 ;
// 开始创建代码
string nsName = "Temp" + System.Guid.NewGuid().ToString("N");
// 生成C#代码
string strSource = GenerateCode(nsName, strFileName , RecordTypes );
// 编译临时生成的C#代码
System.Collections.Specialized.StringCollection strReferences = new System.Collections.Specialized.StringCollection();
System.CodeDom.Compiler.CompilerParameters options = new System.CodeDom.Compiler.CompilerParameters();
options.GenerateExecutable = false;
options.GenerateInMemory = true ;
// 添加编译器使用的引用
System.Collections.ArrayList refs = new System.Collections.ArrayList();
foreach( Type t in RecordTypes )
{
refs.Add( t.Assembly.CodeBase );
}
refs.Add( this.GetType().Assembly.CodeBase );
refs.AddRange( new string[]{
"mscorlib.dll",
"System.dll" ,
"System.Data.dll" ,
});
for( int iCount = 0 ; iCount < refs.Count ; iCount ++ )
{
string strRef = ( string ) refs[ iCount ] ;
if( strRef.StartsWith("file:///"))
strRef = strRef.Substring( "file:///".Length );
if( options.ReferencedAssemblies.Contains( strRef ) == false )
{
options.ReferencedAssemblies.Add( strRef );
}
}
//string strSource = myWriter.ToString();
// 调用C#代码编译器编译生成程序集
Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider provider = new Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider();
// 若使用微软.NET框架.1则调用ICodeCompiler
//System.CodeDom.Compiler.ICodeCompiler compiler = provider.CreateCompiler();
//System.CodeDom.Compiler.CompilerResults result = compiler.CompileAssemblyFromSource( options , strSource );
// 若使用VS.NET2005或更新版本编译程序会在这里形成一个编译警告信息,
// 则可以将上面两行代码去掉而使用下面的代码
System.CodeDom.Compiler.CompilerResults result = provider.CompileAssemblyFromSource(options, strSource);
if( result.Errors.Count == 0 )
{
System.Reflection.Assembly asm = result.CompiledAssembly ;
myAssemblies.Add( asm );
// 创建内置的数据库对象操作对象
foreach( Type RecordType in RecordTypes )
{
Type t = asm.GetType( nsName + "." + RecordType.Name + "ORMHelper" );
RecordORMHelper helper = ( RecordORMHelper ) System.Activator.CreateInstance( t );
myRecordHelpers[ RecordType ] = helper ;
System.Console.WriteLine("FastORM为\"" + RecordType.FullName + "\"创建操作帮助对象");
}
}
else
{
System.Console.WriteLine("ORM框架动态编译错误" );
foreach( string strLine in result.Output )
{
System.Console.WriteLine( strLine );
}
}
provider.Dispose();
return RecordTypes.Count ;
}
}
在本函数中,我们遍历实体Lexington注册列表,找到所有没有装备数据库操作帮助器的实体类型,添加到RecordTypes列表中,然后调用GenerateCode函数生成C#代码。
我们确定编译过程要引用的程序集,Mscorlib.dll,System.dll,System.Data.dll是基本的必不可少的引用,所有的参与动态编译的实体对象类型所在的程序集也得引用,快速ORM框架本身所在的程序集也得引用。将所有的引用信息添加到options的ReferencedAssemblies列表中,这里的options变量是编译使用的参数。然后我们使用myWriter.ToString()获得代码生成器生成的C#源代码文本。我们创建一个CSharpCodeProvider对象,准备编译了,对于微软.NET框架1.1和2.0其调用过程是不同的。对于微软.NET框架1.1,其调用过程为
|
Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider provider = new Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider();
System.CodeDom.Compiler.ICodeCompiler compiler = provider.CreateCompiler();
System.CodeDom.Compiler.CompilerResults result = compiler.CompileAssemblyFromSource( options , strSource );
|
而对微软.NET框架2.0其调用过程为
|
Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider provider = new Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider();
System.CodeDom.Compiler.CompilerResults result = provider.CompileAssemblyFromSource(options, strSource);
|
这体现了微软.NET框架1.1和2.0之间的差别。但微软.NET框架2.0是兼容1.1的,因此用于微软.NET1.1的代码可以在微软.NET2.0下编译通过,但编译器会提示警告信息。
这里调用CompileAssemblyFromSource实际上就是调用微软.NET框架中的基于命令行的C#程序编译器csc.exe的封装。其内部会根据编译器参数options保存的信息生成命令行文本然后启动csc.exe进程。然后将csc.exe的输出结果保存在CompilerResults对象中。
若一切顺利,则使用CompilerResults.CompiledAssembly就能获得编译后生成的程序集,然后我们使用反射操作,对每一个实体类型从动态编译生成的程序集中获得对应的数据库帮助器的类型,然后使用System.Activator.CreateInstance函数就能实例化一个数据库操作帮助器,将这个帮助器放置在实体类型注册列表中等待下次选用。
操作数据库
我们使用动态编译技术获得了数据库操作帮助器,现在我们就使用这些帮助器来实现高速的ORM操作。
查询数据 ReadObjects
快速ORM框架中,定义了一个ReadObjects的函数,用于从数据库中读取数据并生成若干个实体对象,其代码为
public System.Collections.ArrayList ReadObjects( string strSQL , Type RecordType )
{
this.CheckConnection();
if( strSQL == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("strSQL");
}
if( RecordType == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("RecordType");
}
RecordORMHelper helper = this.GetHelper( RecordType );
using( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd = this.Connection.CreateCommand())
{
cmd.CommandText = strSQL ;
System.Data.IDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader();
System.Collections.ArrayList list = helper.ReadRecords( reader , 0 );
reader.Close();
return list ;
}
}
private void CheckConnection()
{
if( myConnection == null )
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("Connection is null");
}
if( myConnection.State != System.Data.ConnectionState.Open )
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("Connection is not opened");
}
}
}
这个函数的参数是SQL查询语句和实体对象类型。在这个函数中,首先是调用CheckConnection函数来检查数据库的连接状态,然后使用GetHelper函数获得对应的数据库操作帮助类,然后执行SQL查询,获得一个数据库读取器,然后调用数据操作帮助类的ReadRecords获得一个列表,该列表就包含了查询数据所得的实体对象。这个过程没有使用反射,执行速度非常快,使用这个快速ORM框架,执行速度跟我们传统的手工编写代码创建实体对象的速度是一样的,但大大降低了我们的开发工作量。
在快速ORM框架中,根据ReadObjects函数派生了ReadObject,ReadAllObject等系列读取数据的函数,其原理都是一样的。
删除数据 DeleteObject
在快速ORM框架中定义了一个DeleteObject函数用于删除数据,其代码为
public int DeleteObject( object RecordObject )
{
this.CheckConnection();
if( RecordObject == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("RecordObject");
}
RecordORMHelper helper = this.GetHelper( RecordObject.GetType() );
using( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd = this.Connection.CreateCommand())
{
if( helper.FillDeleteCommand( cmd , RecordObject ) > 0 )
{
return cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
return 0 ;
}
这个函数的参数就是要删除的对象,在函数中,首先调用GetHelper函数获得数据操作帮助器,然后创建一个数据库命令对象,调用帮助类的FillDeleteCommand函数初始化数据库命令对象,然后执行该命令对象即可删除数据,过程简单明了。ORM框架还定义了DeleteObjects函数用于删除多个实体对象,其原理和DeleteObject函数一样。
更新数据 UpdateObject
快速ORM框架定义了UpdateObject函数用于更新数据,其代码为
public int UpdateObject( object RecordObject )
{
this.CheckConnection();
if( RecordObject == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("RecordObject");
}
RecordORMHelper helper = this.GetHelper( RecordObject.GetType());
using( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd = this.Connection.CreateCommand())
{
int fields = helper.FillUpdateCommand( cmd , RecordObject );
if( fields > 0 )
{
return cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
return 0 ;
}
过程很简单,首先使用GetHelepr函数获得数据库帮助器,然后调用它的FillUpdateCommand函数来设置数据库命令对象,然后执行数据库命令对象即可完成删除数据的操作。ORM框架还定义了 UpdateObjects函数用于更新多条数据库记录,其原理和UpdateObject函数是一样的。
新增数据 InsertObject
快速ORM框架定义了InsertObject函数用于新增数据库记录,其代码为
public int InsertObject( object RecordObject )
{
this.CheckConnection();
if( RecordObject == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("RecordObject");
}
RecordORMHelper helper = this.GetHelper( RecordObject.GetType());
using( System.Data.IDbCommand cmd = this.Connection.CreateCommand())
{
int fields = helper.FillInsertCommand( cmd , RecordObject );
if( fields > 0 )
{
return cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}//using
return 0 ;
}
这个函数也很简单,使用GetHelper获得数据库帮助器,调用帮助器的FillInsertCommand函数设置数据库命令对象,然后执行它即可向数据库插入一条记录。另外一个InsertObjects函数用于插入多条数据库记录,其原理是一样的。
使用ORM框架
在这里我们建立一个简单的WinForm程序来测试使用快速ORM框架。首先我们在一个Access数据库中建立一个员工信息表,名称为Empolyees,并相应的定义了一个数据库实体类型DB_Employees。然后画出一个窗口放置一些控件,编写一些代码,运行程序,其运行界面为
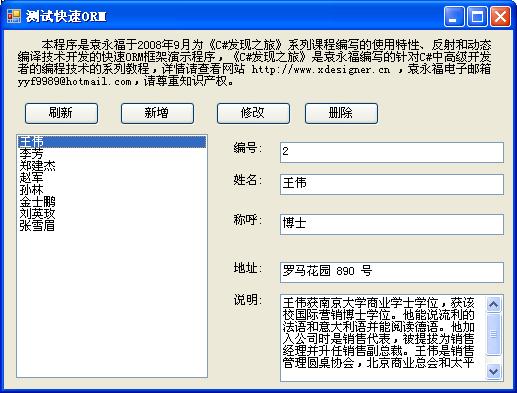
该演示程序主要代码为
///
<summary>/// 连接数据库,创建快速ORM框架对象
///
</summary>
///ORM框架对象
private MyFastORMFramework CreateFramework()
{
System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection conn = new System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection();
conn.ConnectionString = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" + System.IO.Path.Combine( System.Windows.Forms.Application.StartupPath , "demomdb.mdb" );
conn.Open();
return new MyFastORMFramework( conn );
}
// 刷新按钮事件处理
private void cmdRefresh_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
using( MyFastORMFramework myWork = this.CreateFramework())
{
RefreshList( myWork );
}
}
// 用户名列表当前项目改变事件处理
private void lstName_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
DB_Employees obj = lstName.SelectedItem as DB_Employees ;
if( obj != null )
{
this.txtID.Text = obj.EmployeeID.ToString() ;
this.txtName.Text = obj.FullName ;
this.txtTitleOfCourtesy.Text = obj.TitleOfCourtesy ;
this.txtAddress.Text = obj.Address ;
this.txtNotes.Text = obj.Notes ;
}
else
{
this.txtID.Text = "";
this.txtName.Text = "";
this.txtTitleOfCourtesy.Text = "";
this.txtNotes.Text = "" ;
this.txtAddress.Text = "";
}
}
// 新增按钮事件处理
private void cmdInsert_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
try
{
using( dlgRecord dlg = new dlgRecord())
{
dlg.Employe = new DB_Employees();
if( dlg.ShowDialog( this ) == DialogResult.OK )
{
using( MyFastORMFramework myWork = this.CreateFramework())
{
if( myWork.InsertObject( dlg.Employe ) > 0 )
{
RefreshList( myWork );
}
}
}
}
}
catch( Exception ext )
{
MessageBox.Show( ext.ToString());
}
}
// 删除按钮事件处理
private void cmdDelete_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
DB_Employees obj = this.lstName.SelectedItem as DB_Employees ;
if( obj != null )
{
if( MessageBox.Show(
this ,
"是否删除 " + obj.FullName + " 的纪录?",
"系统提示" ,
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBoxButtons.YesNo ) == DialogResult.Yes )
{
using( MyFastORMFramework myWork = this.CreateFramework())
{
myWork.DeleteObject( obj );
RefreshList( myWork );
}
}
}
}
// 刷新员工名称列表
private void RefreshList( MyFastORMFramework myWork )
{
object[] objs = myWork.ReadAllObjects(typeof( DB_Employees ));
System.Collections.ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.AddRange( objs );
this.lstName.DataSource = list ;
this.lstName.DisplayMember = "FullName";
}
// 修改按钮事件处理
private void cmdEdit_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
DB_Employees obj = this.lstName.SelectedItem as DB_Employees ;
if( obj == null )
return ;
using( dlgRecord dlg = new dlgRecord())
{
dlg.txtID.ReadOnly = true ;
dlg.Employe = obj ;
if( dlg.ShowDialog( this ) == DialogResult.OK )
{
using( MyFastORMFramework myWork = this.CreateFramework())
{
if( myWork.UpdateObject( obj ) > 0 )
{
RefreshList( myWork );
}
}
}
}
}
这段代码是比较简单的,而实体类型DB_Employees的代码可以很容易的使用代码生成器生成出来。借助于快速ORM框架,使得基本的数据库记录维护操作开发速度快,运行速度也快。
部署快速ORM框架
这个快速ORM框架是轻量级的,你只需要将MyFastORMFramework.cs以及BindTableAttribute和BindFieldAttribute的代码复制到你的C#工程即可,也可将它们编译成一个DLL,供VB.NET等其他非C#的.NET工程使用。
小结
在本课程中,我们使用反射和动态编译技术实现了一个快速ORM框架,详细学习了一个比较简单的动态编译技术的完整实现。动态编译技术将自由灵活和运行速度结合在一起,是一个比较强大的软件开发技术,综合利用反射和动态编译技术使得我们有可能打造灵活而高速的程序框架。
 Mikel
Mikel




















 为了让大家更深入的了解和使用
为了让大家更深入的了解和使用