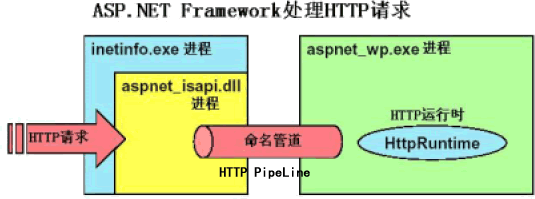
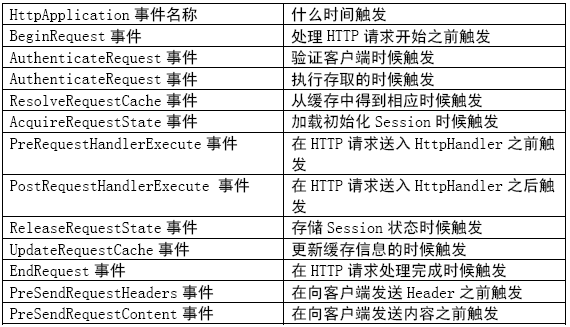
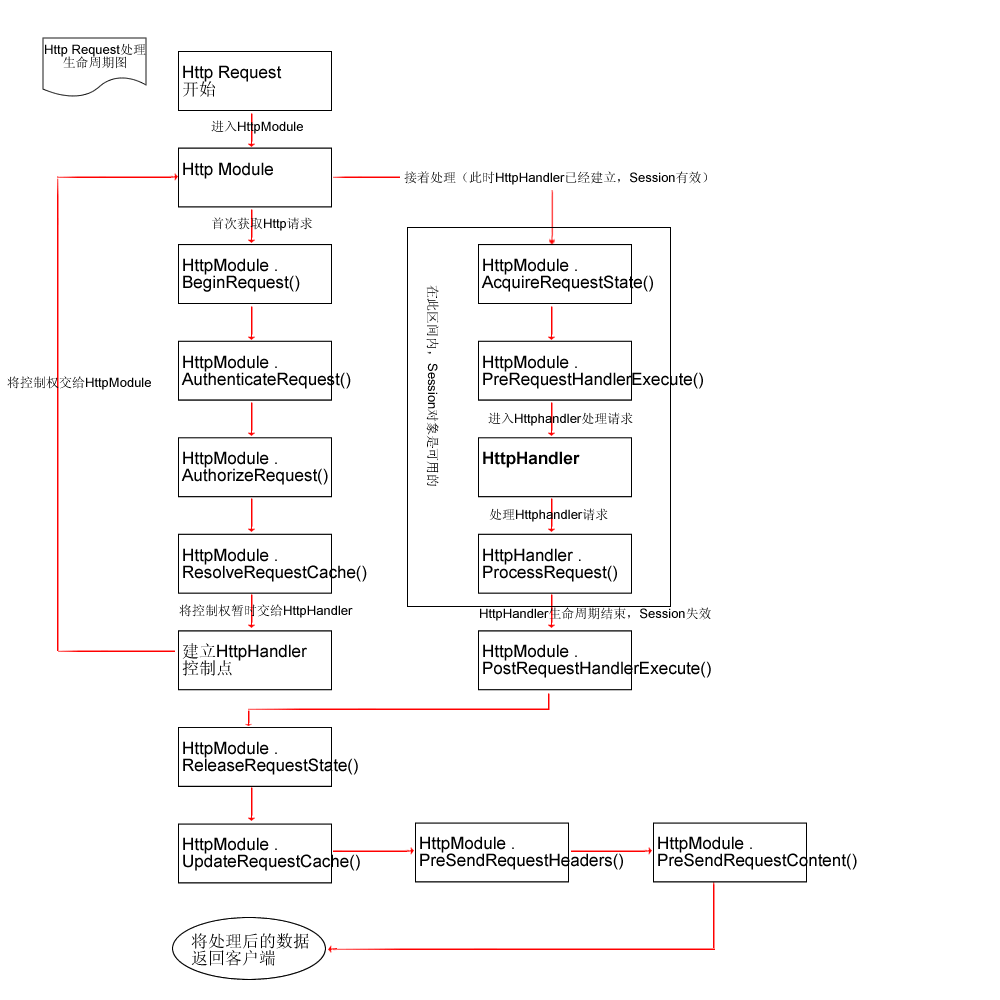
接着上一章留下的线索,我们开始分析 Controller 的执行过程。
1. Controller.Execute
public abstract class Controller : IActionFilter, IController, IDisposable
{
protected internal virtual void Execute(ControllerContext controllerContext)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
ControllerContext = controllerContext;
TempData = new TempDataDictionary(controllerContext.HttpContext);
string actionName = RouteData.GetRequiredString("action");
ControllerActionInvoker invoker = ActionInvoker ?? new ControllerActionInvoker(controllerContext);
if (!invoker.InvokeAction(actionName, new Dictionary<string, object>()))
{
HandleUnknownAction(actionName);
}
}
}
熟 悉的面孔 —— TempData。和 ViewData 的目标不同,TempData 主要用于 Controller 内部的数据传递。从 Router 字典中取出 Action 的名字,并创建一个专门的 Invoker 来完成整个执行工作,包括过滤器(ActionFilterAttribute)、Action Method,以及视图显示(IViewDataContainer)。MVC 给了我们一个选择,我们可以继承并创建一个自定义的 Invoker 去改变一些内在的规则 (在 Controller.ctor 中对 ActionInvoker 赋值)。
2. ControllerActionInvoker.InvokeAction
如 果你看书很仔细的话,难道你对上面 Execute 方法里面的 "invoker.InvokeAction(actionName, new Dictionary<string, object>())" 语句不感到奇怪吗?一个没有任何引用的空 Dictionary,这似乎不合乎情理。传递参数?返回某些值?注意看下面的分析。
public class ControllerActionInvoker
{
public virtual bool InvokeAction(string actionName, IDictionary<string, object> values)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
MethodInfo methodInfo = FindActionMethod(actionName, values);
if (methodInfo != null)
{
IDictionary<string, object> parameters = GetParameterValues(methodInfo, values);
IList<IActionFilter> filters = GetAllActionFilters(methodInfo);
ActionExecutedContext postContext = InvokeActionMethodWithFilters(methodInfo, parameters, filters);
InvokeActionResultWithFilters(postContext.Result, filters);
// notify controller of completion
return true;
}
// notify controller that no method matched
return false;
}
FindActionMethod 方法利用反射返回 Action 方法的信息,注意 NonActionAttribute、Controller_ActionCannotBeGeneric。很显然这个作者有非常好的编码习惯,代码注 释非常清晰有用,值得学习。可以有和 Action 签名相同的重载方法,但必须加上 NonActionAttribute 特性。同时 Action 不能是泛型方法。
protected virtual MethodInfo FindActionMethod(string actionName, IDictionary<string, object> values)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
// We have to loop through all the methods to make sure there isn't
// a conflict. If we stop the loop the first time we find a match
// we might miss some error cases.
MemberInfo[] memberInfos = ControllerContext.Controller.GetType().GetMember(
actionName, MemberTypes.Method,
BindingFlags.IgnoreCase | BindingFlags.InvokeMethod | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public);
MethodInfo foundMatch = null;
foreach (MethodInfo methodInfo in memberInfos)
{
// (1) Action methods must not have the non-action attribute in their inheritance chain,
// and (2) special methods like constructors, property accessors, and event accessors cannot
// be action methods, and (3) methods originally defined on Object (like ToString()) or
// Controller (like Dispose()) cannot be action methods.
if (!methodInfo.IsDefined(typeof(NonActionAttribute), true) &&
!methodInfo.IsSpecialName &&
!methodInfo.GetBaseDefinition().DeclaringType.IsAssignableFrom(typeof(Controller)))
{
if (foundMatch != null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(String.Format(
CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, MvcResources.Controller_MoreThanOneAction,
actionName, ControllerContext.Controller.GetType()));
}
foundMatch = methodInfo;
}
}
if (foundMatch != null)
{
if (foundMatch.ContainsGenericParameters)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(String.Format(
CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, MvcResources.Controller_ActionCannotBeGeneric,
foundMatch.Name));
}
}
return foundMatch;
}
GetParameterValues 方法的作用是从环境上下文中获取 Action 方法执行所需的参数 (Argument)。比如 Action 的方法签名是 "public ActionResult Test(int x, int y)",那么 GetParameterValues 则必须返回一个类似 "{{x, 123}, {y, 456 }}" 这样的参数字典,在反射调用 Test 时,传递过去。
protected virtual IDictionary<string, object> GetParameterValues(methodInfo, values)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
var parameterDict = new Dictionary<string, object>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
foreach (ParameterInfo parameterInfo in methodInfo.GetParameters())
{
if (parameterInfo.IsOut || parameterInfo.ParameterType.IsByRef)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(String.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture,
MvcResources.Controller_ReferenceParametersNotSupported,
parameterInfo.Name,
'methodInfo.Name));
}
parameterDict[parameterInfo.Name] = GetParameterValue(parameterInfo, values);
}
return parameterDict;
}
循环提取所有的 ParameterInfo,不过这里有了另外一个限制,那就是方法参数不能使用 ref / out 关键字。GetParameterValue 方法应该是获取具体参数值,一路传递过来的那个空字典被丢了进去。
protected virtual object GetParameterValue(parameterInfo, values)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
Type parameterType = parameterInfo.ParameterType;
string parameterName = parameterInfo.Name;
string actionName = parameterInfo.Member.Name;
bool valueRequired = !TypeHelpers.TypeAllowsNullValue(parameterType);
// Try to get a value for the parameter. We use this order of precedence:
// 1. Explicitly-provided extra parameters in the call to InvokeAction()
// 2. Values from the RouteData (could be from the typed-in URL or from the route's default values)
// 3. Request values (query string, form post data, cookie)
object parameterValue = null;
if (!(values != null && values.TryGetValue(parameterName, out parameterValue)))
{
if (!(ControllerContext.RouteData != null &&
ControllerContext.RouteData.Values.TryGetValue(parameterName, out parameterValue)))
{
if (ControllerContext.HttpContext != null && ControllerContext.HttpContext.Request != null)
{
parameterValue = ControllerContext.HttpContext.Request[parameterName];
}
}
}
// … 省略部分代码 …
try
{
return ConvertParameterType(parameterValue, parameterType, parameterName, actionName);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
}
return null;
}
再次夸一下作者,那几行注释说明了一切。对于 Action 方法参数的获取,有三种优先级不同的方式:
1. 从调用 InvokeAction 传递进来的参数字典中提取。(就是那个莫名其妙的字典,这意味着自定义 Invoker 有机会对请求参数做出调整)
2. 从 RouteData 中查找,这有两种可能:第一是 URL 请求中已有的参数;其次就是 routes.MapRoute 定义的缺省值。
3. 如果上述两个方法都没有找到参数值,那只好从 Request 中提取了。(某些时候,MapRoute 的定义并不完整,尤其是 {Controller}/{Action} 这种通用规则)
在准备好 Action 的相关数据后,InvokeAction 调用 GetAllActionFilters 获取所有的过滤器。
protected virtual IList<IActionFilter> GetAllActionFilters(MethodInfo methodInfo)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
// use a stack since we're building the member chain backward
Stack<MemberInfo> memberChain = new Stack<MemberInfo>();
// first, push the most derived action method, then its base method, and so forth
memberChain.Push(methodInfo);
MethodInfo baseMethod = methodInfo.GetBaseDefinition();
Type curType = methodInfo.DeclaringType.BaseType;
while (true)
{
MemberInfo[] memberInfos = curType.GetMember(methodInfo.Name, MemberTypes.Method,
BindingFlags.IgnoreCase | BindingFlags.InvokeMethod | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public);
MethodInfo foundMatch = null;
foreach (MethodInfo possibleMatch in memberInfos)
{
if (possibleMatch.GetBaseDefinition() == baseMethod)
{
foundMatch = possibleMatch;
break;
}
}
if (foundMatch == null)
{
// we've passed the declaring type of the base method
break;
}
if (foundMatch.DeclaringType == curType)
{
// only push if there's no jump in the inheritance chain
memberChain.Push(foundMatch);
}
curType = curType.BaseType;
}
// second, push the current controller type, then its base type, and so forth
curType = ControllerContext.Controller.GetType();
while (curType != null)
{
memberChain.Push(curType);
curType = curType.BaseType;
}
// now build the actual filter list up from the beginning. add the current controller
// if it implements IActionFilter, then process the memberInfo stack.
List<IActionFilter> filterList = new List<IActionFilter>();
IActionFilter controllerFilter = ControllerContext.Controller as IActionFilter;
if (controllerFilter != null)
{
filterList.Add(controllerFilter);
}
foreach (MemberInfo memberInfo in memberChain)
{
filterList.AddRange(GetActionFiltersForMember(memberInfo));
}
return filterList;
}
这个方法看上去有点复杂。
1. 创建一个后进先出的栈。
2. 将 Action 压进去。
3. 循环向上查找所有级别的 Base Type,并将 Base Action Method 压到栈里。
4. 接下来将当前 Controller Type 以及其所有 Base Type 先后压到栈里。
5. 创建一个列表用于存储实际的 IActionFilter 集合。
6. 将当前 Controller 添加到列表,别忘了默认情况下控制器本身也实现了 IActionFilter。
7. 使用循环依次从栈中弹出 Base Type、Base Action Method 以及 Current Action Method,并调用 GetActionFiltersForMember 获取其所有 ActionFilterAttribute 定义。
8. 返回一个过滤器列表。(由于是后进先出的栈,因此列表内部顺序是:Current Controller、Base Type Filter、Base Action Method Filter、Current Action Method Filter)
注意 ActionFilterAttribute 是可以应用的 Class 上的,也就是说对所有的 Action 方法都有效。现在你该理解上面获取基类型的原因了吧。
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Method, …)]
public abstract class ActionFilterAttribute : Attribute, IActionFilter { … }
当然,我们还是要看看 GetActionFiltersForMember。
protected virtual IList<IActionFilter> GetActionFiltersForMember(MemberInfo memberInfo)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
List<IActionFilter> unorderedFilters = new List<IActionFilter>();
SortedList<int, IActionFilter> orderedFilters = new SortedList<int, IActionFilter>();
ActionFilterAttribute[] attrs = (ActionFilterAttribute[])memberInfo.GetCustomAttributes(
typeof(ActionFilterAttribute), false /* inherit */);
foreach (ActionFilterAttribute filter in attrs)
{
// filters are allowed to have the same order only if the order is -1. in that case,
// they are processed before explicitly ordered filters but in no particular order in
// relation to one another.
if (filter.Order >= 0)
{
if (orderedFilters.ContainsKey(filter.Order))
{
MethodBase methodInfo = memberInfo as MethodBase;
// … 省略抛出异常代码 …
}
orderedFilters.Add(filter.Order, filter);
}
else
{
unorderedFilters.Add(filter);
}
}
// now append the ordered list to the unordered list to create the final list
unorderedFilters.AddRange(orderedFilters.Values);
return unorderedFilters;
}
这 个方法很简单,用反射查找 ActinFilterAttribute。唯一需要注意的是 order 这个排序属性,返回的列表是按此属性排序过的。ActionFilterAttribute.Order 默认等于 -1,也就说不修改这个排序属性的话,会按照其定义顺序返回。另外还有一个需要注意的地方,如果 ActionFilterAttribute.Order > 0,那么多个 Filter.Order 不能相同,否则会抛出类似下面这样的异常。
The action method 'Test' on controller 'Learn.MVC.Controllers.HomeController' has two filter attributes with filter order 1. If a filter specifies an order of 0 or greater, no other filter on that action method may specify that same order.
回到正题,InvokeAction 获得全部 Filter 后,InvokeActionMethodWithFilters 被调用。
protected virtual ActionExecutedContext InvokeActionMethodWithFilters(methodInfo, parameters, filters)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
ActionExecutingContext preContext = new ActionExecutingContext(ControllerContext,
methodInfo, parameters);
Func<ActionExecutedContext> continuation = () =>
new ActionExecutedContext(ControllerContext, methodInfo, null /* exception */)
{
Result = InvokeActionMethod(methodInfo, parameters)
};
// need to reverse the filter list because the continuations are built up backward
Func<ActionExecutedContext> thunk = filters.Reverse().Aggregate(continuation,
(next, filter) => () => InvokeActionMethodFilter(filter, preContext, next));
return thunk();
}
将 Action Method 用委托进行包装,反转过滤器列表进行集合累计调用。Aggregate + InvokeActionMethodFilter 通过递归调用完成 Filter OnActionExecuting -> Current Action Execute -> Filter OnActionExecuted 这样一个执行过程。下面是调用结果示例。
CurrentController.OnActionExecuting
BaseClassFilter.OnActionExecuting
CurrentClassFilter.OnActionExecuting
BaseActionFilter.OnActionExecuting
CurrentActionFilter.OnActionExecuting
InvokeActionMethod -> Action
CurrentActionFilter.OnActionExecuted
BaseActionFilter.OnActionExecuted
CurrentClassFilter.OnActionExecuted
BaseClassFilter.OnActionExecuted
CurrentController.OnActionExecuted
InvokeAction 紧接着会通过调用 InvokeActionResultWithFilters 完成对 Filter.OnResultExecuting 和 OnResultExecuted 的调用,这是 P2 所没有的。
InvokeActionResultWithFilters 和 InvokeActionMethodWithFilters 过程差不多,都是递归调用。需要特别注意的是 InvokeActionResult 代替了 InvokeActionMethod。(注意:尽管 BaseController 本身也是一个 ActionFilterAttribute,但并不会被调用)
protected virtual ResultExecutedContext InvokeActionResultWithFilters(ActionResult actionResult, IList<IActionFilter> filters)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
ResultExecutingContext preContext = new ResultExecutingContext(ControllerContext, actionResult);
Func<ResultExecutedContext> continuation = delegate
{
InvokeActionResult(actionResult);
return new ResultExecutedContext(ControllerContext, preContext.Result, null /* exception */);
};
// need to reverse the filter list because the continuations are built up backward
Func<ResultExecutedContext> thunk = filters.Reverse().Aggregate(continuation,
(next, filter) => () => InvokeActionResultFilter(filter, preContext, next));
return thunk();
}
执行结果顺序演示:
CurrentController.OnResultExecuting
BaseClassFilter.OnResultExecuting
CurrentClassFilter.OnResultExecuting
BaseActionFilter.OnResultExecuting
CurrentActionFilter.OnResultExecuting
InvokeActionResult -> ActionResult.ExecuteResult() -> IViewEngine.RenderView()
CurrentActionFilter.OnResultExecuted
BaseActionFilter.OnResultExecuted
CurrentClassFilter.OnResultExecuted
BaseClassFilter.OnResultExecuted
CurrentController.OnResultExecuted
我们看看 InvokeActionResult 做了些什么。
protected virtual void InvokeActionResult(ActionResult actionResult)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
actionResult.ExecuteResult(ControllerContext);
}
调 用 ActionResult.ExecuteResult 方法?有什么作用呢?如果你已经看过 P3 的帮助文件的话,你应该知道 Action Method 可以通过 Controller.View()、Controller.Json()、Controller.RedirectToRouteResult() 方法返回如下几种 ActionResult。
public class ViewResult : ActionResult {}
public class JsonResult : ActionResult {}
public class RedirectToRouteResult : ActionResult {}
先不管后面两种,看看 ViewResult.ExecuteResult() 会做什么?
public class ViewResult : ActionResult
{
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
// … 省略部分代码 …
string viewName = (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(ViewName)) ?
ViewName : context.RouteData.GetRequiredString("action");
ViewContext viewContext = new ViewContext(context, viewName, MasterName, ViewData, TempData);
ViewEngine.RenderView(viewContext);
}
HoHo~~~~ 终于看到了视图显示的曙光了,不过这属于下一篇的内容。
———————–
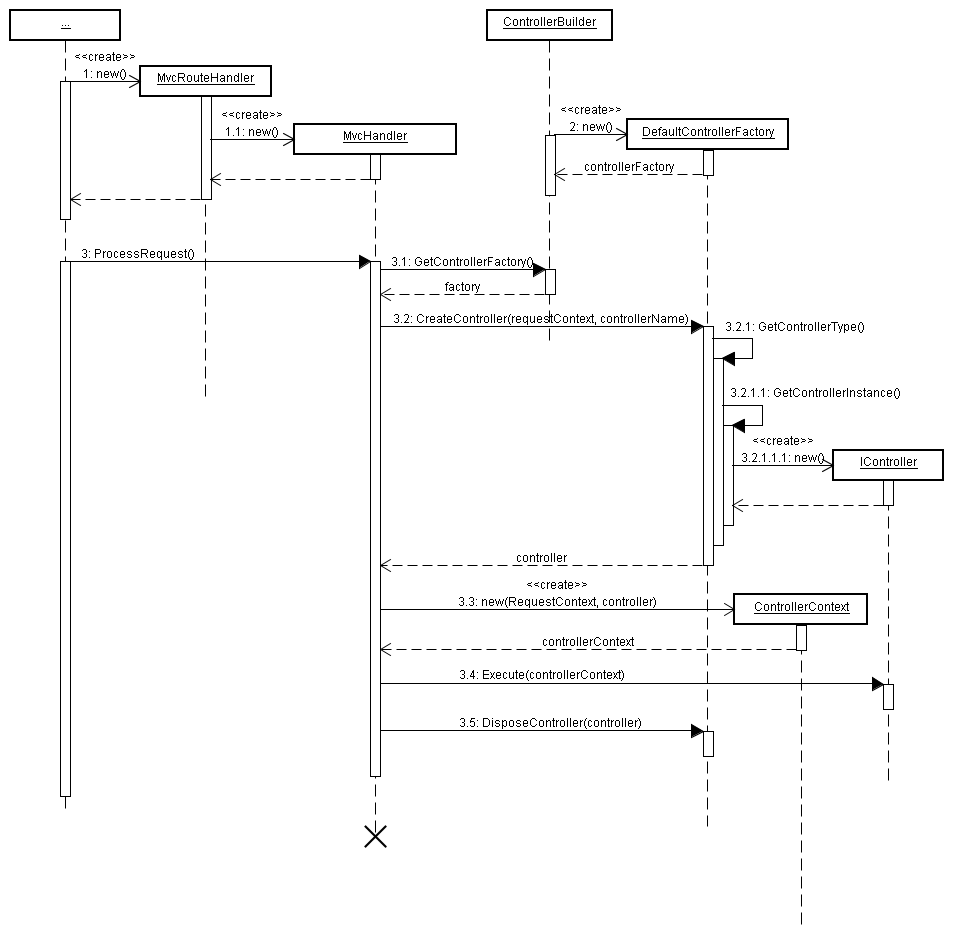
ControllerActionInvoker.InvokeAction()、Controller.Execute() 执行至此结束。
执行流程图
查看大图
 Mikel
Mikel








 }
} }
}