系列目录#
- 第一章|理论基础+实战控制台程序实现AutoFac注入
- 第二章|AutoFac的使用技巧
- 第三章|实战Asp.Net Framework Web程序实现AutoFac注入
- 第四章|实战Asp.Net Core自带DI实现依赖注入
- 第五章|实战Asp.Net Core引入AutoFac的两种方式
本来计划是五篇文章的,每章发个半小时随便翻翻就能懂,但是第一篇发了之后,我发现.NET环境下很多人对IoC和DI都很排斥,搞得评论区异常热闹。
同一个东西,在Java下和在.NET下能有这么大的差异,也是挺有意思的一件事情。
所以我就把剩下四篇内容精简再精简,合成一篇了,权当是写给自己的一个备忘记录了。
GitHub源码地址:https://github.com/WangRui321/Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac
源码是一个虚构的项目框架,类似于样例性质的代码或者测试程序,里面很多注释,对理解DI,或怎么在MVC、WebApi和Core Api分别实现依赖注入有很好的帮助效果。
所以,以下内容,配合源码食用效果更佳~
第一部分:详解AutoFac用法#
名词解释#
老规矩,理论先行。
组件(Components)#
一串声明了它所提供服务和它所消费依赖的代码。
可以理解为容器内的基本单元,一个容器内会被注册很多个组件,每个组件都有自己的信息:比如暴露的服务类型、生命周期域、绑定的具象对象等。

服务(Services)#
一个在提供和消费组件之间明确定义的行为约定。
和项目中的xxxService不同,AutoFac的服务是对容器而言的,可以简单的理解为上一章讲的组件的暴露类型(即对外开放的服务类型),也就是As方法里的东西:
Copy
builder.RegisterType<CallLogger>()
.As<ILogger>()
.As<ICallInterceptor>();
这里,针对同一个注册对象(CallLogger),容器就对外暴露了两个服务(service),ILogger服务和ICallInterceptor服务。
生命周期作用域(LifeTimeScope)#
指服务实例在你的应用中存在的时长:从开始实例化到最后释放结束。
指它在应用中能共享给其他组件并被消费的作用域。例如, 应用中有个全局的静态单例,那么该全局对象实例的 “作用域” 将会是整个应用。
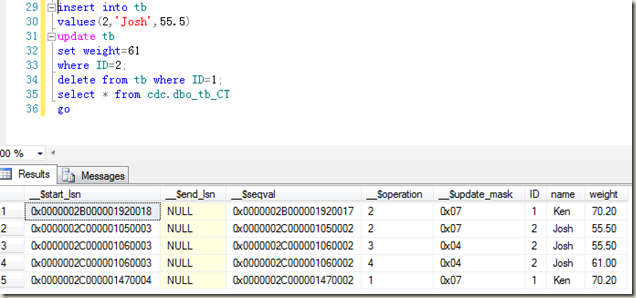
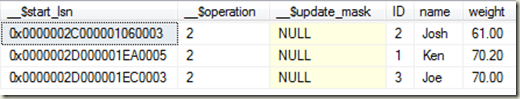
其实是把这两个概念组合在了一起, 可以理解为应用中的一个工作单元。后面详细讲。
怎么理解它们的关系#
容器是一个自动售货机,组件是放在里面的在售商品,服务是商品的出售名称。
把商品(项目里的具象对象)放入自动售货机(容器)上架的过程叫注册;
注册的时候会给商品贴上标签,标注该商品的名称,这个名称就叫服务;
我们还可以标注这个商品的适用人群和过期时间等(生命周期作用域);
把这个包装后的商品放入自动售货机后,它就变成了在售商品(组件)。
当有顾客需要某个商品时,他只要对着售货机报一个商品名(服务名),自动售货机找到对应商品,抛出给客户,这个抛给你的过程,就叫做注入你;
而且这个售货机比较智能,抛出前还可以先判断商品是不是过期了,该不该抛给你。
注册组件#
即在容器初始化时,向容器内添加对象的操作。AutoFac封装了以下几种便捷的注册方法:
反射注册#
直接指定注入对象与暴露类型,使用RegisterType<T>()或者RegisterType(typeof(T))方法:
Copy
builder.RegisterType<StudentRepository>()
.As<IStudentRepository>();
builder.RegisterType(typeof(StudentService))
.As(typeof(IStudentService));
实例注册#
将实例注册到容器,使用RegisterInstance()方法,通常有两种:
Copy
var output = new StringWriter();
builder.RegisterInstance(output).As<TextWriter>();
Copy
builder.RegisterInstance(MySingleton.Instance).ExternallyOwned();
Lambda表达式注册#
Copy
builder.Register(x => new StudentRepository())
.As<IStudentRepository>();
builder.Register(x => new StudentService(x.Resolve<IStudentRepository>()))
.As<IStudentService>();
利用拉姆达注册可以实现一些常规反射无法实现的操作,比如一些复杂参数注册。
泛型注册#
最常见的就是泛型仓储的注册:
Copy
builder.RegisterGeneric(typeof(BaseRepository<>))
.As(typeof(IBaseRepository<>))
.InstancePerLifetimeScope();
条件注册#
通过加上判断条件,来决定是否执行该条注册语句。
表示:如果没注册过xxx,就执行语句:
Copy
builder.RegisterType<TeacherRepository>()
.AsSelf()
.IfNotRegistered(typeof(ITeacherRepository));
只有当ITeacherRepository服务类型没有被注册过,才会执行该条注册语句。
表示:只有…,才会执行语句:
Copy
builder.RegisterType<TeacherService>()
.AsSelf()
.As<ITeacherService>()
.OnlyIf(x =>
x.IsRegistered(new TypedService(typeof(ITeacherRepository)))||
x.IsRegistered(new TypedService(typeof(TeacherRepository))));
只有当ITeacherRepository服务类型或者TeacherRepository服务类型被注册过,才会执行该条注册语句。
程序集批量注册#
最常用,也最实用的一个注册方法,使用该方法最好要懂点反射的知识。
Copy
public static void BuildContainerFunc8(ContainerBuilder builder)
{
Assembly[] assemblies = Helpers.ReflectionHelper.GetAllAssemblies();
builder.RegisterAssemblyTypes(assemblies)
.Where(cc =>cc.Name.EndsWith("Repository")|
cc.Name.EndsWith("Service"))
.PublicOnly()
.Where(cc=>cc.IsClass)
.AsImplementedInterfaces();
builder.RegisterGeneric(typeof(BaseRepository<>))
.As(typeof(IBaseRepository<>));
}
如上会批量注册项目中所有的Repository和Service。
属性注入#
讲属性注入之前,要先看下构造注入。
- 构造注入
即解析的时候,利用构造函数注入,形式如下:
Copy
public class StudentService : IStudentService
{
private readonly IStudentRepository _studentRepository;
public StudentService(IStudentRepository studentRepository)
{
_studentRepository = studentRepository;
}
}
在构造函数的参数中直接写入服务类型,AutoFac解析该类时,就会去容器内部已存在的组件中查找,然后将匹配的对象注入到构造函数中去。
- 属性注入
属性注入与构造注入不同,是将容器内对应的组件直接注入到类内的属性中去,形式如下:
Copy
public class TeacherService : ITeacherService
{
public ITeacherRepository TeacherRepository { get; set; }
public string GetTeacherName(long id)
{
return TeacherRepository?.Get(111).Name;
}
}
要使用这种属性注入,在注册该属性所属类的时候,需要使用PropertiesAutowired()方法额外标注,如下:
Copy
builder.RegisterType<TeacherService>().PropertiesAutowired();
这样,容器在解析并实例化TeacherService类时,便会将容器内的组件与类内的属性做映射,如果相同则自动将组件注入到类内属性种。
属性注入争议性很大,很多人称这是一种_反模式_,事实也确实如此。
使用属性注入会让代码可读性变得极其复杂(而复杂难懂的代码一定不是好的代码,不管用的技术有多高大上)。
但是属性注入也不是一无是处,因为属性注入有一个特性:
在构造注入的时候,如果构造函数的参数中有一个对象在容器不存在,那么解析就会报错。
但是属性注入就不一样了,当容器内没有与该属性类型对应的组件时,这时解析不会报异常,只会让这个属性保持为空类型(null)。
利用这个特性,可以实现一些特殊的操作。
暴露服务#
即上面提到的As<xxx>()函数,AutoFac提供了以下三种标注暴露服务类型的方法:
以其自身类型暴露服务#
使用AsSelf()方法标识,表示以其自身类型暴露,也是当没有标注暴露服务的时候的默认选项。
如下四种写法是等效的:
Copy
builder.RegisterType<StudentService>();//不标注,默认以自身类型暴露服务
builder.RegisterType<StudentService>().AsSelf();
builder.RegisterType<StudentService>().As<StudentService>();
builder.RegisterType<StudentService>().As(typeof(StudentService));
以其实现的接口(interface)暴露服务#
使用As()方法标识,暴露的类型可以是多个,比如CallLogger类实现了ILogger接口和ICallInterceptor接口,那么可以这么写:
Copy
builder.RegisterType<CallLogger>()
.As<ILogger>()
.As<ICallInterceptor>()
.AsSelf();
程序集批量注册时指定暴露类型#
Copy
public static void BuildContainerFunc8(ContainerBuilder builder)
{
Assembly[] assemblies = Helpers.ReflectionHelper.GetAllAssemblies();
builder.RegisterAssemblyTypes(assemblies)
.Where(cc =>cc.Name.EndsWith("Repository")|
cc.Name.EndsWith("Service"))
.As(x=>x.GetInterfaces()[0])
}
使用AsImplementedInterfaces()函数实现,相当于一个类实现了几个接口(interface)就会暴露出几个服务,等价于上面连写多个As()的作用。
Copy
public static void BuildContainerFunc8(ContainerBuilder builder)
{
Assembly[] assemblies = Helpers.ReflectionHelper.GetAllAssemblies();
builder.RegisterAssemblyTypes(assemblies)
.Where(cc =>cc.Name.EndsWith("Repository")|
cc.Name.EndsWith("Service"))
.AsImplementedInterfaces();
}
生命周期作用域#
相当于UnitWork(工作单元)的概念。下面罗列出了AutoFac与.NET Core的生命周期作用域,并作了简要的对比。
AutoFac的生命周期作用域#
下面讲下AutoFac定义的几种生命周期作用域,上一篇评论里也有人提了,关于生命周期作用域这块确实不是很好理解,所以下面每中类型我都写了一个例子程序,这些例子程序对理解很有帮助,只要能读懂这些例子程序,就一定能弄懂这些生命周期作用域。(例子项目源码里都有,可以去试着实际运行下,更易理解)
瞬时实例(Instance Per Dependency)
也叫每个依赖一个实例。
即每次从容器里拿出来的都是全新对象,相当于每次都new出一个。
在其他容器中也被标识为 ‘Transient'(瞬时) 或 ‘Factory’(工厂)。
使用InstancePerDependency()方法标注,如果不标注,这也是默认的选项。以下两种注册方法是等效的:
Copy
//不指定,默认就是瞬时的
builder.RegisterType<Model.StudentEntity>();
//指定其生命周期域为瞬时
builder.RegisterType<Model.StudentEntity>().InstancePerDependency();
Copy
using (var scope = Container.Instance.BeginLifetimeScope())
{
var stu1 = scope.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
Console.WriteLine($"第1次打印:{stu1.Name}");
stu1.Name = "张三";
Console.WriteLine($"第2次打印:{stu1.Name}");
var stu2 = scope.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
Console.WriteLine($"第2次打印:{stu2.Name}");
}
上面解析了2次,有两个实例,stu1和stu2指向不同的两块内存,彼此之间没有关系。
打印结果:

单例(Single Instance)
即全局只有一个实例,在根容器和所有嵌套作用域内,每次解析返回的都是同一个实例。
使用SingleInstance()方法标识:
Copy
builder.RegisterType<Model.StudentEntity>().SingleInstance();
Copy
var stu1 = Container.Instance.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
stu1.Name = "张三";
Console.WriteLine($"第1次打印:{stu1.Name}");
using (var scope1 = Container.Instance.BeginLifetimeScope())
{
var stu2 = scope1.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
Console.WriteLine($"第2次打印:{stu2.Name}");
stu1.Name = "李四";
}
using (var scope2 = Container.Instance.BeginLifetimeScope())
{
var stu3 = scope2.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
Console.WriteLine($"第3次打印:{stu3.Name}");
}
上面的stu1、stu2、stu3都是同一个实例,在内存上它们指向同一个内存块。
打印结果:

域内单例(Instance Per Lifetime Scope)
即在每个生命周期域内是单例的。
- 注册
使用InstancePerLifetimeScope()方法标识:
Copy
x.RegisterType<Model.StudentEntity>().InstancePerLifetimeScope();
Copy
using (var scope1 = Container.Instance.BeginLifetimeScope())
{
var stu1 = scope1.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
Console.WriteLine($"第1次打印:{stu1.Name}");
stu1.Name = "张三";
var stu2 = scope1.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
Console.WriteLine($"第2次打印:{stu2.Name}");
}
using (var scope2 = Container.Instance.BeginLifetimeScope())
{
var stuA = scope2.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
Console.WriteLine($"第3次打印:{stuA.Name}");
stuA.Name = "李四";
var stuB = scope2.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
Console.WriteLine($"第4次打印:{stuB.Name}");
}
如上,在子域一中,虽然解析了2次,但是2次解析出的都是同一个实例,即stu1和stu2指向同一个内存块Ⅰ。
子域二也一样,stuA和stuB指向同一个内存块Ⅱ,但是内存块Ⅰ和内存块Ⅱ却不是同一块。
打印结果如下,第1次和第3次为null:

指定域内单例(Instance Per Matching Lifetime Scope)
即每个匹配的生命周期作用域一个实例。
该域类型其实是上面的“域内单例”的其中一种,不一样的是它允许我们给域“打标签”,只要在这个特定的标签域内就是单例的。
- 注册
使用InstancePerMatchingLifetimeScope(string tagName)方法注册:
Copy
builder.RegisterType<Worker>().InstancePerMatchingLifetimeScope("myTag");
Copy
using (var myScope1 = Container.Instance.BeginLifetimeScope("myTag"))
{
var stu1 = myScope1.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
stu1.Name = "张三";
Console.WriteLine($"第1次打印:{stu1.Name}");
var stu2 = myScope1.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
Console.WriteLine($"第2次打印:{stu2.Name}");
}
using (var myScope2 = Container.Instance.BeginLifetimeScope("myTag"))
{
var stuA = myScope2.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
Console.WriteLine($"第3次打印:{stuA.Name}");
}
using (var noTagScope = Container.Instance.BeginLifetimeScope())
{
try
{
var stuOne = noTagScope.Resolve<Model.StudentEntity>();
Console.WriteLine($"第4次正常打印:{stuOne.Name}");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine($"第4次异常打印:{e.Message}");
}
}
打印结果:

需要注意:
- 第3次打印为null,不同子域即使标签相同,但也是不同子域,所以域之间不是同一个实例
- 在其他标签的域内(包括无标签域)解析,会报异常
每次请求内单例(Instance Per Request)
该种类型适用于“request”类型的应用,比如MVC和WebApi。
其实质其实又是上一种的“指定域内单例”的一种特殊情况:AutoFac内有一个静态字符串叫Autofac.Core.Lifetime.MatchingScopeLifetimeTags.RequestLifetimeScopeTag,其值为"AutofacWebRequest",当“指定域内单例”打的标签是这个字符串时,那它就是“每次请求内单例”了。

- 注册
使用InstancePerRequest()方法标注:
Copy
builder.RegisterType<Model.StudentEntity>().InstancePerRequest();
也可以使用上面的域内单例的注册法(但是不建议):
Copy
builder.RegisterType<Model.StudentEntity>().InstancePerMatchingLifetimeScope(Autofac.Core.Lifetime.MatchingScopeLifetimeTags.RequestLifetimeScopeTag);
builder.RegisterType<Model.StudentEntity>().InstancePerMatchingLifetimeScope("AutofacWebRequest");
这里用控制台程序不好举例子就不写解析代码了,要理解“每次请求内单例”的作用,最好的例子就是EF中的DBContext,我们在一次request请求内,即使是用到了多个Service和多个Repository,也只需要一个数据库实例,这样即能减少数据库实例初始化的消耗,还能实现事务的功能。
.NET Core的生命周期作用域(Service lifetimes)#
相比于AutoFac的丰富复杂,.NET Core就比较简单粗暴了,只要3种类型:
瞬时实例(Transient)
与AutoFac的瞬时实例(Instance Per Dependency)相同,每次都是全新的实例。
使用AddTransient()注册:
Copy
services.AddTransient<IStudentService, StudentService>();
请求内单例(Scoped)
其意义与AutoFac的请求内单例(Instance Per Request)相同,但实际如果真正在.NET Core中使用使用AutoFac的话,应该使用AutoFac的域内单例(Instance Per LifetimeScope)来代替。
原因是.NET Core框架自带的DI(Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection)全权接管了请求和生命周期作用域的创建,所以AutoFac无法控制,但是使用域内单例(Instance Per LifetimeScope)可以实现相同的效果。
使用AddScoped()注册:
Copy
services.AddScoped<IStudentService, StudentService>();
单例(Singleton)
与AutoFac的单例(Single Instance)相同。
使用AddSingleton();注册:
Copy
services.AddSingleton<StudentEntity>();
第二部分:.NET Framework Web程序AutoFac注入#
MVC项目#
思路很简单,三步走:
- 新建AutoFac容器
- 初始化容器,向容器注册所有需要的依赖对象
- 将AutoFac解析器设置为系统的依赖解析器(Dependency Resolver)

MVC容器#

除了AutoFac主包之外,还需要Nuget导入AutoFac.Mvc5包:

容器代码:
Copy
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using Autofac;
using Autofac.Integration.Mvc;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Repository.IRepository;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Repository.Repository;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.Ioc
{
public static class MvcContainer
{
public static IContainer Instance;
public static System.Web.Mvc.IDependencyResolver Init(Func<ContainerBuilder, ContainerBuilder> func = null)
{
var builder = new ContainerBuilder();
MyBuild(builder);
func?.Invoke(builder);
Instance = builder.Build();
return new AutofacDependencyResolver(Instance);
}
public static void MyBuild(ContainerBuilder builder)
{
Assembly[] assemblies = Helpers.ReflectionHelper.GetAllAssembliesWeb();
builder.RegisterAssemblyTypes(assemblies)
.Where(cc => cc.Name.EndsWith("Repository") |
cc.Name.EndsWith("Service"))
.PublicOnly()
.Where(cc => cc.IsClass)
.AsImplementedInterfaces();
builder.RegisterGeneric(typeof(BaseRepository<>)).As(typeof(IBaseRepository<>));
Assembly mvcAssembly = assemblies.FirstOrDefault(x => x.FullName.Contains(".NetFrameworkMvc"));
builder.RegisterControllers(mvcAssembly);
}
}
}
这里Init()初始化函数返回类型变成了System.Web.Mvc.IDependencyResolver接口,即MVC的系统依赖解析器。
AutoFac自己封装了一个AutofacDependencyResolver类(AutoFac依赖解析器类)实现了这个接口,所以直接new一个AutofacDependencyResolver类返回,等下把这个AutoFac依赖解析器类设置为MVC的系统依赖解析器就可以了。
Copy
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Globalization;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace Autofac.Integration.Mvc
{
public class AutofacDependencyResolver : IDependencyResolver
{
}
项目主程序:#

启动时初始化容器,并把AutoFac生成的解析器设置为系统依赖解析器:
Copy
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Web.Optimization;
using System.Web.Routing;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.Ioc;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.NetFrameworkMvc
{
public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
protected void Application_Start()
{
AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas();
FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters);
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles);
System.Web.Mvc.IDependencyResolver autoFacResolver = MvcContainer.Init();
DependencyResolver.SetResolver(autoFacResolver);
}
}
}
其中DependencyResolver.SetResolver()为MVC封装的一个静态方法,用于设置MVC的依赖解析器。
其参数只要是实现了System.Web.Mvc.IDependencyResolver接口的对象都可以,AutoFac自己封装的解析器AutofacDependencyResolver类实现了这个接口,所以可以传进来,从而实现了让AutoFac接管MVC的依赖注入。
直接利用构造注入就可以了:
Copy
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Service.IService;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.NetFrameworkMvc.Controllers
{
public class StudentController : Controller
{
private readonly IStudentService _studentService;
public StudentController(IStudentService studentService)
{
_studentService = studentService;
}
public string GetStuNameById(long id)
{
return _studentService.GetStuName(id);
}
}
}
运行调用Api#

WebApi项目#
和MVC一样,思路很简单,三步走:
- 新建AutoFac容器
- 初始化容器,向容器注册所有需要的依赖对象
- 将AutoFac解析器设置为系统的依赖解析器(Dependency Resolver)

Api容器#

除了AutoFac主包之外,还需要Nuget导入AutoFac.WebApi2包:

容器代码:
Copy
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using Autofac;
using Autofac.Integration.WebApi;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Repository.Repository;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Repository.IRepository;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.Ioc
{
public static class ApiContainer
{
public static IContainer Instance;
public static System.Web.Http.Dependencies.IDependencyResolver Init(Func<ContainerBuilder, ContainerBuilder> func = null)
{
var builder = new ContainerBuilder();
MyBuild(builder);
func?.Invoke(builder);
Instance = builder.Build();
return new AutofacWebApiDependencyResolver(Instance);
}
public static void MyBuild(ContainerBuilder builder)
{
var assemblies = Helpers.ReflectionHelper.GetAllAssembliesWeb();
builder.RegisterAssemblyTypes(assemblies)
.Where(cc => cc.Name.EndsWith("Repository") |
cc.Name.EndsWith("Service"))
.PublicOnly()
.Where(cc => cc.IsClass)
.AsImplementedInterfaces();
builder.RegisterGeneric(typeof(BaseRepository<>)).As(typeof(IBaseRepository<>));
Assembly mvcAssembly = assemblies.FirstOrDefault(x => x.FullName.Contains(".NetFrameworkApi"));
builder.RegisterApiControllers(mvcAssembly);
}
}
}
这里Init()初始化函数返回类型变成了System.Web.Http.Dependencies.IDependencyResolver接口,即WebApi的系统依赖解析器。
AutoFac自己封装了一个AutofacWebApiDependencyResolver类(AutoFac针对WebApi的依赖解析器类)实现了这个接口,所以直接new一个AutofacWebApiDependencyResolver类返回,等下把这个AutoFac依赖解析器类设置为WebApi的系统依赖解析器就可以了。
WebApi主程序#

在项目启动时初始化容器:
Copy
using System.Web.Http;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Web.Optimization;
using System.Web.Routing;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.Ioc;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.NetFrameworkApi
{
public class WebApiApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
protected void Application_Start()
{
AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas();
GlobalConfiguration.Configure(WebApiConfig.Register);
FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters);
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles);
System.Web.Http.Dependencies.IDependencyResolver autoFacResolver = ApiContainer.Init();
HttpConfiguration config = GlobalConfiguration.Configuration;
config.DependencyResolver = autoFacResolver;
}
}
}
这里跟上面的MVC项目不太一样,是通过HttpConfiguration对象来设置依赖解析器的,但是原理相同,不赘述了。
直接利用构造函数注入即可:
Copy
using System.Web.Http;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Service.IService;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.NetFrameworkApi.Controllers
{
public class StudentController : ApiController
{
private readonly IStudentService _studentService;
public StudentController(IStudentService studentService)
{
_studentService = studentService;
}
[HttpGet]
[Route("Student/GetStuNameById")]
public string GetStuNameById(long id)
{
return _studentService.GetStuName(123);
}
}
}
运行调用接口#

第三部分:.NET Core的DI#

自带的DI#
与.NET Framework不同,.NET Core把DI提到了非常重要的位置,其框架本身就集成了一套DI容器。
针对其自带DI,主要理解两个对象,IServiceCollection和 IServiceProvider。
用于向容器注册服务,可以和AutoFac的ContainerBuilder(容器构建器)类比。
负责从容器中向外部提供实例,可以和AutoFac的解析的概念类比。
注册的地方就在主程序下的startup类中。
但是其本身的注册语法并没有AutoFac那么丰富,泛型注册、批量注册这些全都没有,只有下面这种最基础的一个一个注册的形式:
Copy
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.CoreIoc.Extensions;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.CoreIoc.Helpers;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.CoreApi
{
public class Startup
{
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2);
services.AddScoped<ITeacherRepository, TeacherRepository>();
services.AddScoped<IStudentRepository, StudentRepository>();
services.AddScoped<IBaseRepository<StudentEntity>, BaseRepository<StudentEntity>>();
services.AddScoped<IBaseRepository<TeacherEntity>, BaseRepository<TeacherEntity>>();
services.AddScoped<IBaseRepository<BookEntity>, BaseRepository<BookEntity>>();
services.AddScoped<IStudentService, StudentService>();
services.AddScoped<ITeacherService, TeacherService>();
services.AddScoped<IBookService, BookService>();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseMvc();
}
}
}
所以,大家通常都会自己去扩展这些注册方法,以实现一些和AutoFac一样的便捷的注册操作,下面我根据反射写了一个小扩展,写的比较简单潦草,可以参考下:
扩展代码:
Copy
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Model;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Repository.IRepository;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Repository.Repository;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Service.IService;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Service.Service;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.CoreIoc.Extensions
{
public static class RegisterExtension
{
public static IServiceCollection AddAssemblyServices(this IServiceCollection services, Assembly assembly, ServiceLifetime serviceLifetime = ServiceLifetime.Scoped)
{
var typeList = new List<Type>();
List<Type> types = assembly.GetTypes().
Where(t => t.IsClass && !t.IsGenericType)
.ToList();
typeList.AddRange(types);
if (!typeList.Any()) return services;
var typeDic = new Dictionary<Type, Type[]>();
foreach (var type in typeList)
{
var interfaces = type.GetInterfaces();
typeDic.Add(type, interfaces);
}
foreach (var instanceType in typeDic.Keys)
{
Type[] interfaceTypeList = typeDic[instanceType];
if (interfaceTypeList == null)
{
services.AddServiceWithLifeScoped(null, instanceType, serviceLifetime);
}
else
{
foreach (var interfaceType in interfaceTypeList)
{
services.AddServiceWithLifeScoped(interfaceType, instanceType, serviceLifetime);
}
}
}
return services;
}
private static void AddServiceWithLifeScoped(this IServiceCollection services, Type interfaceType, Type instanceType, ServiceLifetime serviceLifetime)
{
switch (serviceLifetime)
{
case ServiceLifetime.Scoped:
if (interfaceType == null) services.AddScoped(instanceType);
else services.AddScoped(interfaceType, instanceType);
break;
case ServiceLifetime.Singleton:
if (interfaceType == null) services.AddSingleton(instanceType);
else services.AddSingleton(interfaceType, instanceType);
break;
case ServiceLifetime.Transient:
if (interfaceType == null) services.AddTransient(instanceType);
else services.AddTransient(interfaceType, instanceType);
break;
default:
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(serviceLifetime), serviceLifetime, null);
}
}
}
}
利用这个扩展,我们在startup里就可以用类似AutoFac的语法来注册了。
主程序#
注册代码:
Copy
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.CoreIoc.Extensions;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.CoreIoc.Helpers;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.CoreApi
{
public class Startup
{
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2);
Assembly[] assemblies = ReflectionHelper.GetAllAssembliesCoreWeb();
Assembly repositoryAssemblies = assemblies.FirstOrDefault(x => x.FullName.Contains(".Repository"));
services.AddAssemblyServices(repositoryAssemblies);
Assembly serviceAssemblies = assemblies.FirstOrDefault(x => x.FullName.Contains(".Service"));
services.AddAssemblyServices(serviceAssemblies);
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseMvc();
}
}
}
其实AutoFac针对.NET Core已经帮我们集成了一套注册的扩展,我们可以通过两种方式把AutoFac引入.NET Core:一种是将AutoFac容器作为辅助容器,与.NET Core的DI共存,我们可以同时向两个容器里注册组件;一种是让AutoFac容器接管.NET Core的DI,注册时只选择往Autofac容器中注册。
下面就分别实现下这两种引入AutoFac的方式。
AutoFac作为辅助注册#
Core容器#
先按照之前写AutoFac容器的方法,新建一个针对Core的AutoFac容器:
Copy
using System;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Autofac;
using Autofac.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Repository.IRepository;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Repository.Repository;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.CoreIoc
{
public static class CoreContainer
{
public static IContainer Instance;
public static IServiceProvider Init(IServiceCollection services, Func<ContainerBuilder, ContainerBuilder> func = null)
{
var builder = new ContainerBuilder();
builder.Populate(services);
MyBuild(builder);
func?.Invoke(builder);
Instance = builder.Build();
return new AutofacServiceProvider(Instance);
}
public static void MyBuild(this ContainerBuilder builder)
{
var assemblies = Helpers.ReflectionHelper.GetAllAssembliesCoreWeb();
builder.RegisterAssemblyTypes(assemblies)
.Where(cc => cc.Name.EndsWith("Repository") |
cc.Name.EndsWith("Service"))
.PublicOnly()
.Where(cc => cc.IsClass)
.AsImplementedInterfaces();
builder.RegisterGeneric(typeof(BaseRepository<>)).As(typeof(IBaseRepository<>));
}
}
}
主程序#
在主程序中新建一个StartupWithAutoFac类,用于注册。
StartupWithAutoFac代码:
Copy
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Autofac;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.CoreIoc;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.CoreApi
{
public class StartupWithAutoFac
{
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public StartupWithAutoFac(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2);
}
public void ConfigureContainer(ContainerBuilder builder)
{
builder.MyBuild();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseMvc();
}
}
}
这里其他地方与原startup都相同,只是多了一个ConfigureContainer()方法,在该方法内可以按照AutoFac的语法进行自由注册。
然后修改program类,将AutoFac hook进管道,并将StartupWithAutoFac类指定为注册入口:
Copy
using Microsoft.AspNetCore;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.CoreApi
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateWebHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
}
public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.HookAutoFacIntoPipeline()
.UseStartup<StartupWithAutoFac>();
}
}
AutoFac接管注册#
还是上面的CoreContainer容器。
主程序#
主程序新建一个StartupOnlyAutoFac类,
代码如下:
Copy
using System;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Infrastructure.CoreIoc;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.CoreApi
{
public class StartupOnlyAutoFac
{
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public StartupOnlyAutoFac(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IServiceProvider ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2);
return CoreContainer.Init(services);
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseMvc();
}
}
}
这里直接改了ConfigureServices()方法的返回类型,然后在该方法内直接利用AutoFac注册。
最后当然也要更改下program类,指定StartupOnlyAutoFac类为注册入口。
代码:
Copy
using Microsoft.AspNetCore;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.CoreApi
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateWebHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
}
public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseStartup<StartupOnlyAutoFac>();
}
}
运行调用#
Copy
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.Service.IService;
namespace Ray.EssayNotes.AutoFac.CoreApi.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
public class StudentController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IStudentService _studentService;
public StudentController(IStudentService studentService)
{
_studentService = studentService;
}
[Route("Student/GetStuNameById")]
public string GetStuNameById(long id)
{
return _studentService.GetStuName(id);
}
}
}

 Mikel
Mikel

![clipboard[22] clipboard[22]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/296070/201503/041121212092141.png)



















 using System;
using System;
 class Program
class Program
 }
} }
}




























![clip_image008[1] clip_image008[1]](https://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/artech/WindowsLiveWriter/IntroductiontoChangeDataCaptureCDCinSQLS_F5ED/clip_image008%5B1%5D_thumb.jpg)


