[转载]Android平台下实现一个进程管理器 – 疯狂の小石子 – 博客园.
在本人的博客文章《枚举Android系统的进程、任务和服务的息》http://www.cnblogs.com/crazypebble/archive/2011/03/29/1999151.html中, 实现了一个简单的监控Android平台下的系统进程,任务,服务信息的小工具。在本文中,我将对这个小工具中的系统进程信息部分,进一步的完善。从用户 的角度出发,将系统的任务信息Task和服务信息Service全部显示出来的意义不是很大,因此本文将不会对任务和服务两部分内容对任何更新。
介绍之前,先给大家看看程序执行后的界面,首先了解大致的功能,然后理解起来,会更加得心应手。
1、 获取系统进程列表,并加载进程名、CPU占用情况、内存使用情况

2、 点击某一个进程之后,让用户选择操作:“查看详情”和“结束进程”

3、 显示进程的详细信息:包括了进程的安装包路径、版权信息、用户权限、拥有的服务、和拥有的活动,等


4、 程序退出的方式

5、 任务列表 和 服务列表




在对界面和主要功能有一个大致了解之后,我们就开始编写我们的代码了。
一、界面布局
本文对整个功能界面采用了选项卡式的布局,布局文件如下:
<!--?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?-->
每一个选项卡的内容都是一个列表ListView,分别用于显示系统的进程、任务和服务列表,布局文件我们就此略过了。
在进程的详情中,我们使用不同背景色的TextView作为一个数据部分的标题,这样给人视觉上一个比较清晰的层次感,代码如下:
整个详情信息是一个ScrollView,在第一行中嵌入了一个Button,其他行的数据显示都比较简单,大家看看我的控件ID就差不多知道这个控件的意思了。
<!--?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?-->
<button></button>
二、获取进程的图标、进程名、Application名字、和CPU内存信息
我在程序中使用了一个类BasicProgramUtil来存放进程列表中显示的摘要信息,包括了进程图标、进程名、Application名、CPU和内存信息。
/**
* 应用程序包的简要信息
*/
package crazypebble.sysassist.procmgr;
import android.graphics.drawable.Drawable;
public class BasicProgramUtil{
/*
* 定义应用程序的简要信息部分
*/
private Drawable icon; // 程序图标
private String programName; // 程序名称
private String processName;
private String cpuMemString;
public BasicProgramUtil() {
icon = null;
programName = "";
processName = "";
cpuMemString = "";
}
public Drawable getIcon() {
return icon;
}
public void setIcon(Drawable icon) {
this.icon = icon;
}
public String getProgramName() {
return programName;
}
public void setProgramName(String programName) {
this.programName = programName;
}
public String getCpuMemString() {
return cpuMemString;
}
public void setCpuMemString(String cpuMemString) {
this.cpuMemString = cpuMemString;
}
public String getProcessName() {
return processName;
}
public void setProcessName(String processName) {
this.processName = processName;
}
}
1、进程图标
每一个进程,都属于一个应用程序,每个应用程序都有一个图标信息。我们通过 ApplicationInfo.loadIcon(PackageManager)方法返回一个Drawable对象实例,可以获取到一个应用程序的图 标,这里我们直接作为进程的图标进行显示。
2、进程名和Application名字

首先要弄清进程名和Application名字的区别。在Android平台 下,一个进程的进程名实际上以“.”作为分隔符的,类似包名的字符串,这个字符串并不能被普通用户所理解。而Application名字,就是我们刚开始 新建工程时,填入Application部分的内容,是可以被用户接受的应用程序的名字。

由于Application Name更容易被用户接受和读懂,因此我们将Application Name作为进程信息的主显部分。
通过ActivityManager.getRunningAppProcesses()方法可以得到当前正在运行的所有进程列表,该方法返回一个 List<RunningAppProcessInfo>,在RunningAppProcessInfo对象中存放有进程名信息;再通过进 程名获取到ApplicationInfo,通过方法 ApplicationInfo.loadLabel(PackageManager).toString()就返回了应用程序的名字。
3、CPU和内存信息
获取每个进程的CPU和内存信息,可能就没有API函数给我们使用了。我们需要通过执行adb shell指令,进入shell命令模式,执行命令”top –n 1”来获取所有进程运行状态的列表。
Android平台下的很多系统信息可能是无法通过API函数获取到的,这时通过执行shell命令,并解析输出结果。相关链接:《Android的CPU、硬盘、内存、网络设置、系统信息、硬件信息》(http://www.cnblogs.com/crazypebble/archive/2011/04/07/2007916.html)
先来看看top –n 1(这个地方不是字母L,是数字1,请各位小心)命令执行的结果吧。

第一行:CPU的总的使用情况
第二行:总内存的使用情况
从第三行开始,就是每个进程所占用内存和CPU的情况
PID:进程ID,CPU%:CPU占用比例,#THR:进程的线程数,VSS:虚拟内存,RSS:物理内存,PCY:浮云,我也不知道什么意思,UID:用户ID,Name:进程名
了解了上面这些信息之后,想必大家也知道怎么获取这个进程的CPU和内存信息了。要是大家有兴趣,还是好好看看《Android的CPU、硬盘、内存、网络设置、系统信息、硬件信息》,相信这个文章对大家有有用的。
好了,这一部分的功能就做好了,接下来编码了,这里放出主要的代码,其他的代码,希望同学们自己去完善了。
/**
* PackageUtils 用于某进程的ApplicationInfo对象,目的为了获取图标和应用程序名称
*/
package crazypebble.sysassist.procmgr;
import java.util.List;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.pm.ApplicationInfo;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
public class PackageUtil {
// ApplicationInfo 类,保存了普通应用程序的信息,主要是指Manifest.xml中application标签中的信息
private List allAppList;
public PackageUtil(Context context) {
// 通过包管理器,检索所有的应用程序(包括卸载)与数据目录
PackageManager pm = context.getApplicationContext().getPackageManager();
allAppList = pm.getInstalledApplications(PackageManager.GET_UNINSTALLED_PACKAGES);
pm.getInstalledPackages(0);
}
/**
* 通过一个程序名返回该程序的一个ApplicationInfo对象
* @param name 程序名
* @return ApplicationInfo
*/
public ApplicationInfo getApplicationInfo(String appName) {
if (appName == null) {
return null;
}
for (ApplicationInfo appinfo : allAppList) {
if (appName.equals(appinfo.processName)) {
return appinfo;
}
}
return null;
}
}
/**
* 获取某进程的CPU和内存使用情况
*/
package crazypebble.sysassist.procmgr;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import android.util.Log;
import crazypebble.sysassist.common.CMDExecute;
public class ProcessMemoryUtil {
private static final int INDEX_FIRST = -1;
private static final int INDEX_PID = INDEX_FIRST + 1;
private static final int INDEX_CPU = INDEX_FIRST + 2;
private static final int INDEX_STAT = INDEX_FIRST + 3;
private static final int INDEX_THR = INDEX_FIRST + 4;
private static final int INDEX_VSS = INDEX_FIRST + 5;
private static final int INDEX_RSS = INDEX_FIRST + 6;
private static final int INDEX_PCY = INDEX_FIRST + 7;
private static final int INDEX_UID = INDEX_FIRST + 8;
private static final int INDEX_NAME = INDEX_FIRST + 9;
private static final int Length_ProcStat = 9;
private List PMUList = null;
public ProcessMemoryUtil() {
}
private String getProcessRunningInfo() {
Log.i("fetch_process_info", "start. . . . ");
String result = null;
CMDExecute cmdexe = new CMDExecute();
try {
String[] args = {"/system/bin/top", "-n", "1"};
result = cmdexe.run(args, "/system/bin/");
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.i("fetch_process_info", "ex=" + ex.toString());
}
return result;
}
private int parseProcessRunningInfo(String infoString) {
String tempString = "";
boolean bIsProcInfo = false;
String[] rows = null;
String[] columns = null;
rows = infoString.split("[\n]+"); // 使用正则表达式分割字符串
for (int i = 0; i < rows.length; i++) {
tempString = rows[i];
if (tempString.indexOf("PID") == -1) {
if (bIsProcInfo == true) {
tempString = tempString.trim();
columns = tempString.split("[ ]+");
if (columns.length == Length_ProcStat) {
PMUList.add(columns);
}
}
} else {
bIsProcInfo = true;
}
}
return PMUList.size();
}
// 初始化所有进程的CPU和内存列表,用于检索每个进程的信息
public void initPMUtil() {
PMUList = new ArrayList();
String resultString = getProcessRunningInfo();
parseProcessRunningInfo(resultString);
}
// 根据进程名获取CPU和内存信息
public String getMemInfoByName(String procName) {
String result = "";
String tempString = "";
for (Iterator iterator = PMUList.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
String[] item = (String[]) iterator.next();
tempString = item[INDEX_NAME];
if (tempString != null && tempString.equals(procName)) {
result = "CPU:" + item[INDEX_CPU]
+ " Mem:" + item[INDEX_RSS];
break;
}
}
return result;
}
// 根据进程ID获取CPU和内存信息
public String getMemInfoByPid(int pid) {
String result = "";
String tempPidString = "";
int tempPid = 0;
int count = PMUList.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { String[] item = PMUList.get(i); tempPidString = item[INDEX_PID]; if (tempPidString == null) { continue; } tempPid = Integer.parseInt(tempPidString); if (tempPid == pid) { result = "CPU:" + item[INDEX_CPU] + " Mem:" + item[INDEX_RSS]; break; } } return result; } }
/* * 为进程获取基本的信息 */ public BasicProgramUtil buildProgramUtilSimpleInfo(int procId, String procNameString) { BasicProgramUtil programUtil = new BasicProgramUtil(); programUtil.setProcessName(procNameString); // 根据进程名,获取应用程序的ApplicationInfo对象 ApplicationInfo tempAppInfo = packageUtil.getApplicationInfo(procNameString); if (tempAppInfo != null) { // 为进程加载图标和程序名称 programUtil.setIcon(tempAppInfo.loadIcon(packageManager)); programUtil.setProgramName(tempAppInfo.loadLabel(packageManager).toString()); } else { // 如果获取失败,则使用默认的图标和程序名 programUtil.setIcon(getApplicationContext().getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.unknown)); programUtil.setProgramName(procNameString); Log.v(ProcMgrActivity.TAG_SYSTEMASSIST, procNameString); } String str = processMemoryUtil.getMemInfoByPid(procId); Log.v(TAG_SYSTEMASSIST, "Time --- > " + Calendar.getInstance().getTimeInMillis());
programUtil.setCpuMemString(str);
return programUtil;
}
三、获取进程的详细信息
我将进程的详细信息封装在一个类DetailProgramUtil中,主要 包括了进程ID,进程名,版权信息、程序的安装目录和数据目录,安装时间和更新时间、应用程序的权限、应用程序包含的活动Activity、应用程序包含 的服务Service、和安装包的大小信息。
/**
* 应用程序包的详细信息
*/
package crazypebble.sysassist.procmgr;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import android.content.pm.ActivityInfo;
import android.content.pm.ServiceInfo;
import android.text.format.DateFormat;
public class DetailProgramUtil implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/*
* 定义应用程序的扩展信息部分
*/
private int pid;
private String processName; // 程序运行的进程名
private String companyName; // 公司名称
private int versionCode; // 版本代号
private String versionName; // 版本名称
private String dataDir; // 程序的数据目录
private String sourceDir; // 程序包的源目录
private String firstInstallTime; // 第一次安装的时间
private String lastUpdateTime; // 最近的更新时间
private String userPermissions; // 应用程序的权限
private String activities; // 应用程序包含的Activities
private String services; // 应用程序包含的服务
// android.content.pm.PackageState类的包信息
// 此处只是安装包的信息
private String codeSize;
private long dataSize;
private long cacheSize;
private long externalDataSize;
private long externalCacheSize;
private long externalMediaSize;
private long externalObbSize;
public DetailProgramUtil() {
pid = 0;
processName = "";
companyName = "";
versionCode = 0;
versionName = "";
dataDir = "";
sourceDir = "";
firstInstallTime = "";
lastUpdateTime = "";
userPermissions = "";
activities = "";
services = "";
initPackageSize();
}
private void initPackageSize() {
codeSize = "0.00";
dataSize = 0;
cacheSize = 0;
externalCacheSize = 0;
externalDataSize = 0;
externalMediaSize = 0;
externalObbSize = 0;
}
public int getPid() {
return pid;
}
public void setPid(int pid) {
this.pid = pid;
}
public int getVersionCode() {
return versionCode;
}
public void setVersionCode(int versionCode) {
this.versionCode = versionCode;
}
public String getVersionName() {
return versionName;
}
public void setVersionName(String versionName) {
this.versionName = versionName;
}
public String getCompanyName() {
return companyName;
}
public void setCompanyName(String companyString) {
this.companyName = companyString;
}
public String getFirstInstallTime() {
if (firstInstallTime == null || firstInstallTime.length() <= 0) {
firstInstallTime = "null";
}
return firstInstallTime;
}
public void setFirstInstallTime(long firstInstallTime) {
this.firstInstallTime = DateFormat.format(
"yyyy-MM-dd", firstInstallTime).toString();
}
public String getLastUpdateTime() {
if (lastUpdateTime == null || lastUpdateTime.length() <= 0) {
lastUpdateTime = "null";
}
return lastUpdateTime;
}
public void setLastUpdateTime(long lastUpdateTime) {
this.lastUpdateTime = DateFormat.format(
"yyyy-MM-dd", lastUpdateTime).toString();
}
public String getActivities() {
if (activities == null || activities.length() <= 0) {
activities = "null";
}
return activities;
}
public void setActivities(ActivityInfo[] activities) {
this.activities = Array2String(activities);
}
public String getUserPermissions() {
if (userPermissions == null || userPermissions.length() <= 0) {
userPermissions = "null";
}
return userPermissions;
}
public void setUserPermissions(String[] userPermissions) {
this.userPermissions = Array2String(userPermissions);
}
public String getServices() {
if (services == null || services.length() <= 0) {
services = "null";
}
return services;
}
public void setServices(ServiceInfo[] services) {
this.services = Array2String(services);
}
public String getProcessName() {
if (processName == null || processName.length() <= 0) {
processName = "null";
}
return processName;
}
public void setProcessName(String processName) {
this.processName = processName;
}
public String getDataDir() {
if (dataDir == null || dataDir.length() <= 0) {
dataDir = "null";
}
return dataDir;
}
public void setDataDir(String dataDir) {
this.dataDir = dataDir;
}
public String getSourceDir() {
if (sourceDir == null || sourceDir.length() <= 0) { sourceDir = "null"; } return sourceDir; } public void setSourceDir(String sourceDir) { this.sourceDir = sourceDir; } /* * 三个重载方法,参数不同,调用不同的方法,用于将object数组转化成要求的字符串 */ // 用户权限信息 public String Array2String(String[] array) { String resultString = ""; if (array != null && array.length > 0) {
resultString = "";
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
resultString += array[i];
if (i < (array.length - 1)) { resultString += "\n"; } } } return resultString; } // 服务信息 public String Array2String(ServiceInfo[] array) { String resultString = ""; if (array != null && array.length > 0) {
resultString = "";
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i].name == null) {
continue;
}
resultString += array[i].name.toString();
if (i < (array.length - 1)) { resultString += "\n"; } } } return resultString; } // 活动信息 public String Array2String(ActivityInfo[] array) { String resultString = ""; if (array != null && array.length > 0) {
resultString = "";
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i].name == null) {
continue;
}
resultString += array[i].name.toString();
if (i < (array.length - 1)) {
resultString += "\n";
}
}
}
return resultString;
}
public String getCodeSize() {
return codeSize;
}
public void setCodeSize(long codeSize) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("###.00");
this.codeSize = df.format((double)(codeSize/1024.0));
}
public long getDataSize() {
return dataSize;
}
public void setDataSize(long dataSize) {
this.dataSize = dataSize;
}
public long getCacheSize() {
return cacheSize;
}
public void setCacheSize(long cacheSize) {
this.cacheSize = cacheSize;
}
public long getExternalDataSize() {
return externalDataSize;
}
public void setExternalDataSize(long externalDataSize) {
this.externalDataSize = externalDataSize;
}
public long getExternalCacheSize() {
return externalCacheSize;
}
public void setExternalCacheSize(long externalCacheSize) {
this.externalCacheSize = externalCacheSize;
}
public long getExternalMediaSize() {
return externalMediaSize;
}
public void setExternalMediaSize(long externalMediaSize) {
this.externalMediaSize = externalMediaSize;
}
public long getExternalObbSize() {
return externalObbSize;
}
public void setExternalObbSize(long externalObbSize) {
this.externalObbSize = externalObbSize;
}
public String getPackageSize() {
String resultString = "";
resultString = "Code Size: " + codeSize + "KB\n"
+ "Data Size: " + dataSize + "KB\n"
+ "Cache Size: " + cacheSize + "KB\n"
+ "External Data Size: " + externalDataSize + "KB\n"
+ "External Cache Size: " + externalCacheSize + "KB\n"
+ "External Media Size: " + externalMediaSize + "KB\n"
+ "External Obb Size: " + externalObbSize + "KB";
return resultString;
}
}
目录信息:通过进程的ApplicationInfo对象获取,获取进程ApplicationInfo的方法在类PackageUtil.java中。
版权信息、权限、活动、服务信息:通过PackageInfo对象获取,获取进程PackageInfo的方法:PackageManager.getPackageInfo(packageName, flags)。这个方法需要一定flags信息,我在代码中已经用注释写明了所需要的flags,请各位还是查阅一下SDK的开发文档,里面会有更详细的解释。
方法buildProgramUtilComplexInfo用于为需要查看详情的进程生成一个DetailProgramUtil对象,通过Bundle.putSerializable(key, (Serializable)DetaiProgramUtil),将这个对象传递给另一个活动进行显示。所以在上面DetailProgramUtil.java文件的一开始,该类实现了Serializable的接口。
/*
* 为进程获取安装包的详情
*/
public DetailProgramUtil buildProgramUtilComplexInfo(String procNameString) {
DetailProgramUtil complexProgramUtil = new DetailProgramUtil();
// 根据进程名,获取应用程序的ApplicationInfo对象
ApplicationInfo tempAppInfo = packageUtil.getApplicationInfo(procNameString);
if (tempAppInfo == null) {
return null;
}
PackageInfo tempPkgInfo = null;
try {
tempPkgInfo = packageManager.getPackageInfo(
tempAppInfo.packageName,
PackageManager.GET_UNINSTALLED_PACKAGES | PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES
| PackageManager.GET_SERVICES | PackageManager.GET_PERMISSIONS);
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (tempPkgInfo == null) {
return null;
}
complexProgramUtil.setProcessName(procNameString);
complexProgramUtil.setCompanyName(getString(R.string.no_use));
complexProgramUtil.setVersionName(tempPkgInfo.versionName);
complexProgramUtil.setVersionCode(tempPkgInfo.versionCode);
complexProgramUtil.setDataDir(tempAppInfo.dataDir);
complexProgramUtil.setSourceDir(tempAppInfo.sourceDir);
// 以下注释部分的信息暂时获取不到
// complexProgramUtil.setFirstInstallTime(tempPkgInfo.firstInstallTime);
// complexProgramUtil.setLastUpdateTime(tempPkgInfo.lastUpdateTime);
// complexProgramUtil.setCodeSize(packageStats.codeSize);
// complexProgramUtil.setDataSize(packageStats.dataSize);
// complexProgramUtil.setCacheSize(packageStats.cacheSize);
// complexProgramUtil.setExternalDataSize(0);
// complexProgramUtil.setExternalCacheSize(0);
// complexProgramUtil.setExternalMediaSize(0);
// complexProgramUtil.setExternalObbSize(0);
// 获取以下三个信息,需要为PackageManager进行授权(packageManager.getPackageInfo()方法)
complexProgramUtil.setUserPermissions(tempPkgInfo.requestedPermissions);
complexProgramUtil.setServices(tempPkgInfo.services);
complexProgramUtil.setActivities(tempPkgInfo.activities);
return complexProgramUtil;
}
四、实现进程列表的刷新
进程列表的刷新是一个比较费时的操作,我们将其放在一个独立的线程中执行,并且在刷新过程进行时使用一个ProgressDialog进度对话框覆盖住主视图,等待刷新完成后再返回到主视图。
这一部分使用到了Handler类和线程的相关知识,各位可以参考文章《在Android中使用Handler和Thread线程执行后台操作》。这些不做过多解释,直接上代码,相信大家都能够懂的。
private void updateProcessList() {
// 新建一个进度对话框,在更新列表时,覆盖在父视图之上
pd = new ProgressDialog(ProcMgrActivity.this);
pd.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_SPINNER);
pd.setTitle(getString(R.string.progress_tips_title));
pd.setMessage(getString(R.string.progress_tips_content));
// 启动新线程,执行更新列表操作
handler = new RefreshHandler();
RefreshThread thread = new RefreshThread();
thread.start();
// 显示进度对话框
pd.show();
}
private class RefreshHandler extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// TODO : Update your UI
getListView().setAdapter(procListAdapter);
// 取消进度框
pd.dismiss();
}
}
class RefreshThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO : Do your Stuff here.
procListAdapter = buildProcListAdapter();
Message msg = handler.obtainMessage();
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
五、结束其他进程和退出本程序
这一部分的内容,也已经在我的博客中写了一篇文章《Android下结束进程的方法》,我们在这个任务管理器中使用到的“退出”按钮的实现,强制结束其他进程的方法,都是来自这篇文章。为了方便那些不想点击链接的同学们,我们还是再贴一下代码吧。
退出本程序,主要是通过方法returnToHome方法,该方法将直接退出到主屏幕,请清除当前的活动:
private void returnToHome() {
Intent home = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN);
home.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP);
home.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
startActivity(home);
}
结束其他进程,主要是通过ActivityManager.killBackgroundProcesses(PackageName)方法来实现,还是强烈建议各位看看SDK的开发文档,或者上面的那篇文章。
六、任务列表和服务列表
任务列表和服务列表的信息获取,已经在之前的一篇博客中讲到了,这些再不厌其烦的介绍一下方法,至于原理部分,请各位去看看开发文档吧。
1、任务列表
任务列表功能所显示的全部信息都来自一个类RunningTaskInfo。
ActivityManager activityManager = (ActivityManager) getSystemService(ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
taskList = activityManager.getRunningTasks(maxTaskNum);
2、服务列表
服务列表功能所显示的全部信息都来自一个类RunningServiceInfo。
ActivityManager activityManager = (ActivityManager) getSystemService(ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
serviceList = activityManager.getRunningServices(maxServiceNum);
好了,这个任务管理到这里就告一段落了。这个程序算是本人自学习Android开发以来的处女作,完全是自己动手开发的一个小工具,写下总结,以留作纪 念,也希望可以与更多的同道中人交流技术。如果在文章中,有错误之处,还希望各位可以批评指正,本人一定悉心接受,轻点砸砖~。
===============================优雅的分割线===============================
【声明】本文系本人原创,转载请注明文章出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/crazypebble/archive/2011/04/09/2010196.html

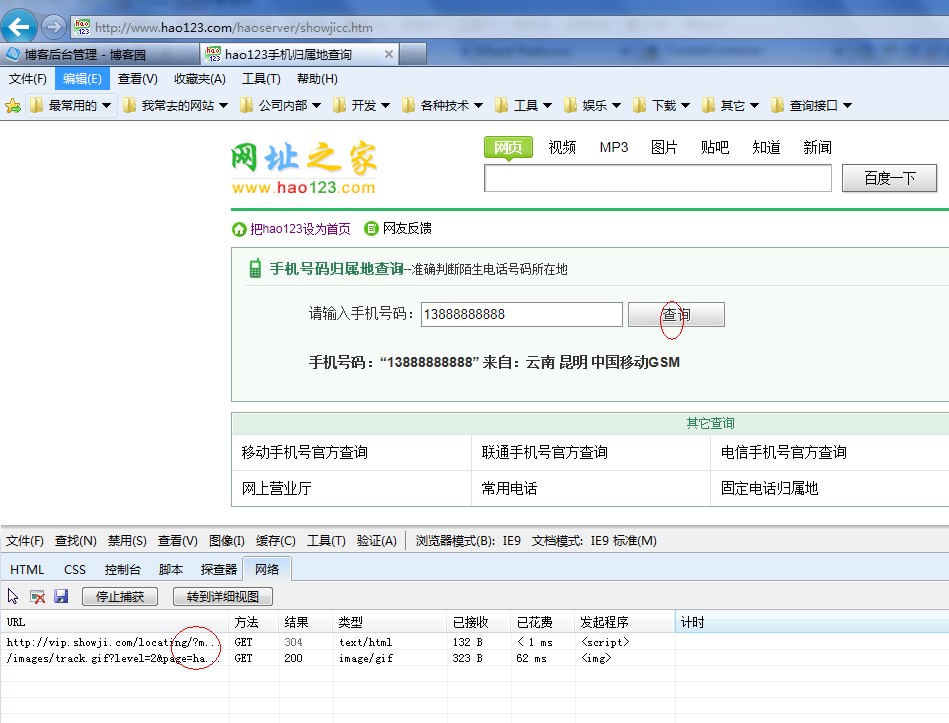

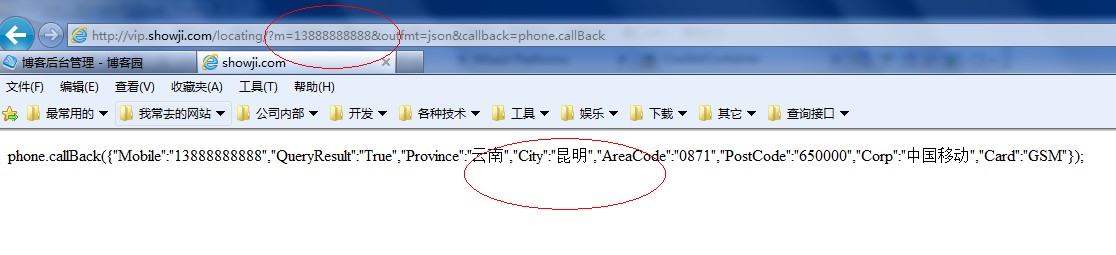
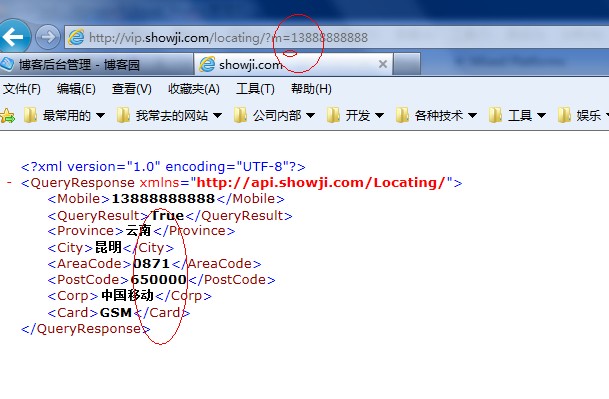

 Mikel
Mikel