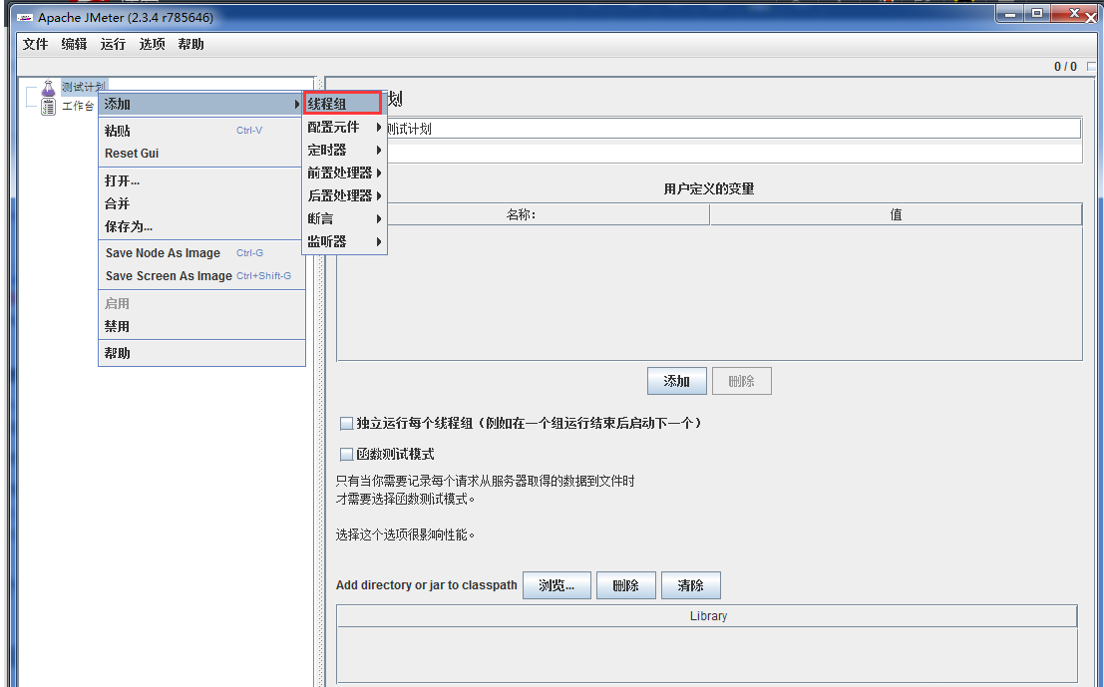
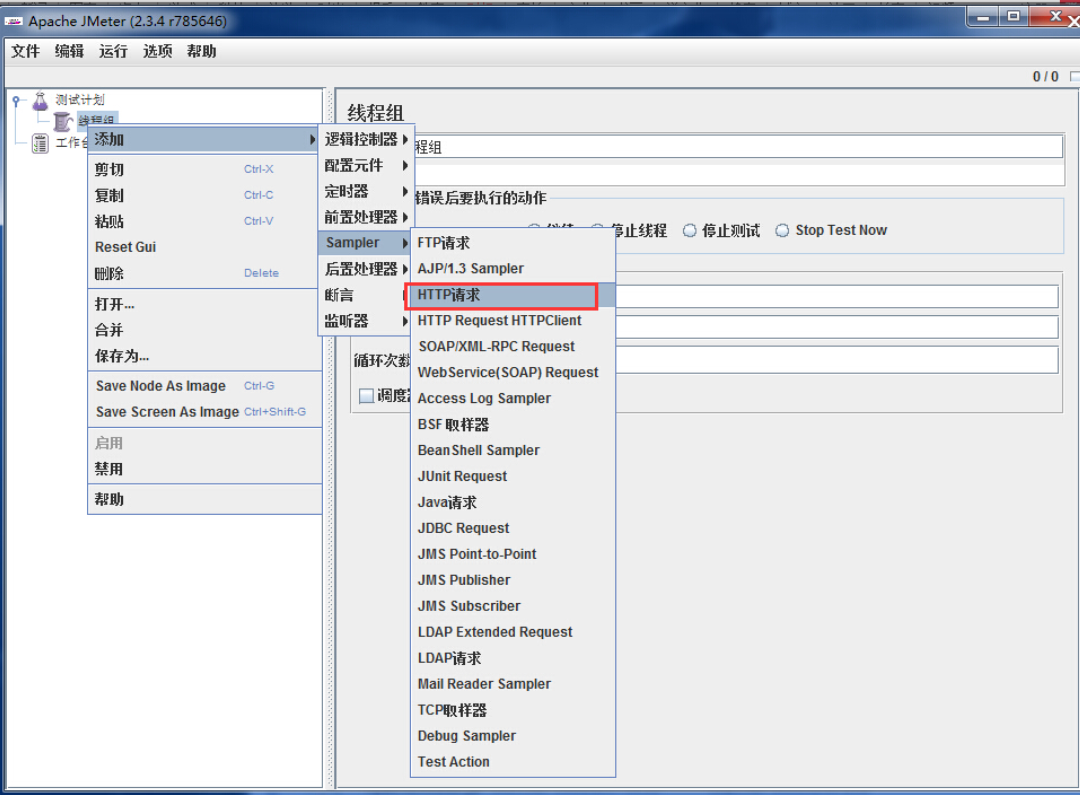
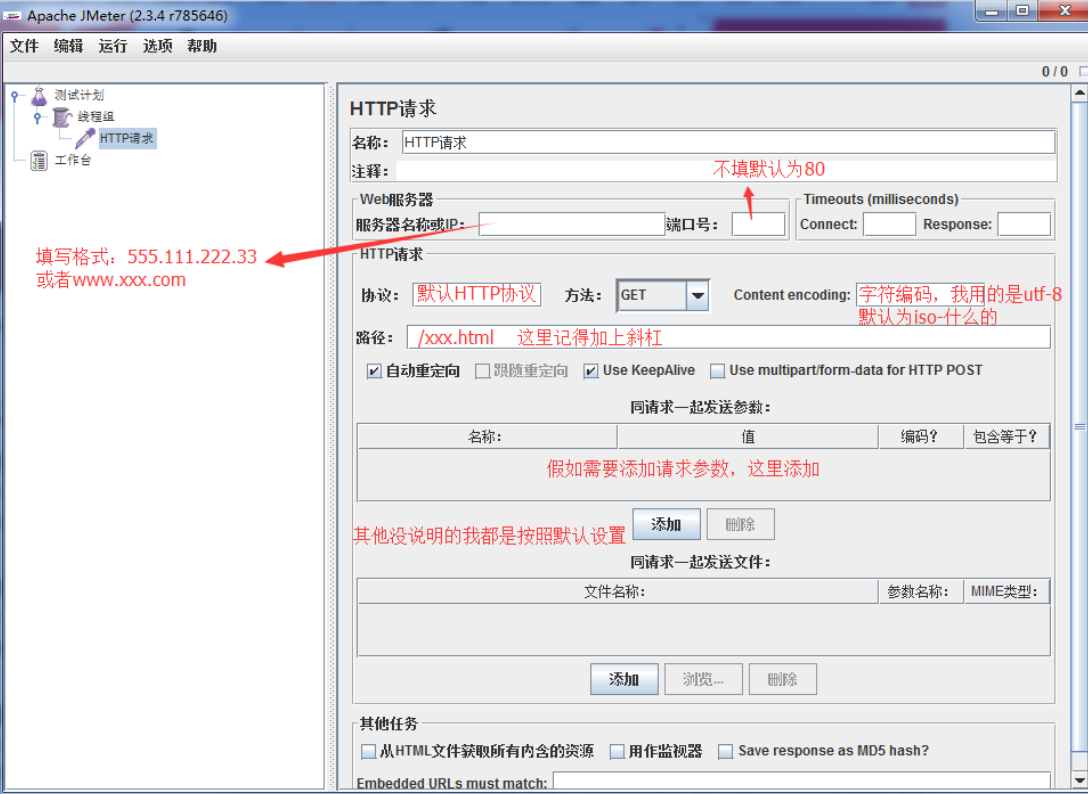
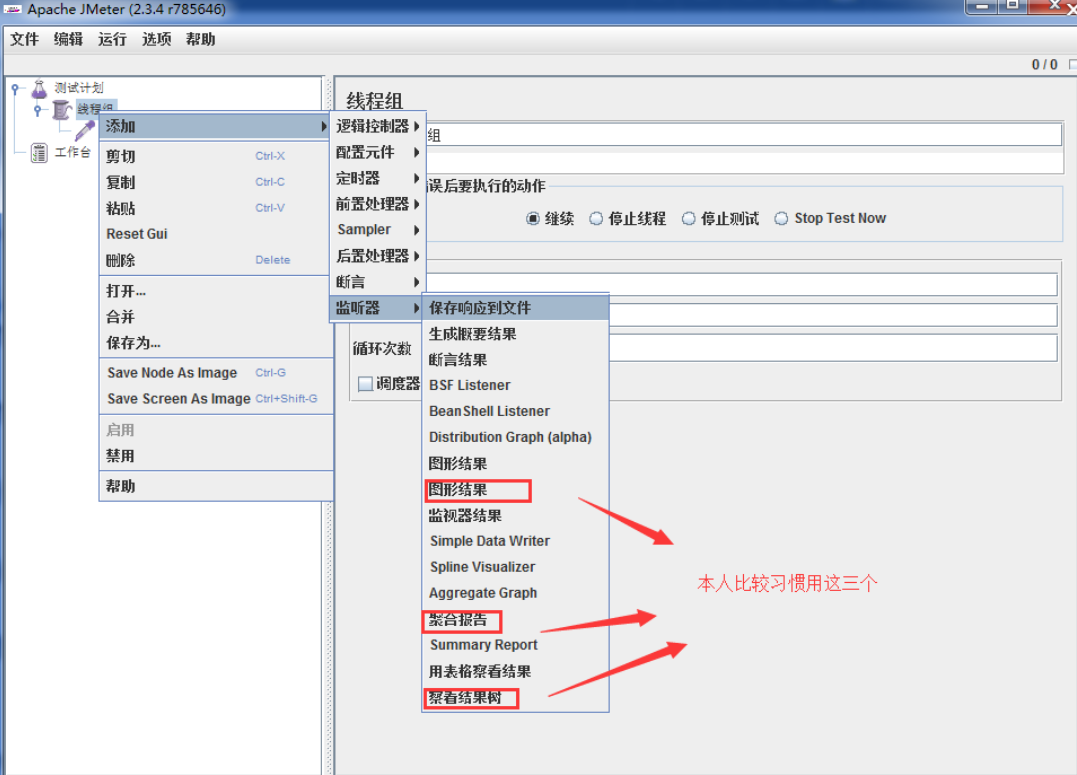
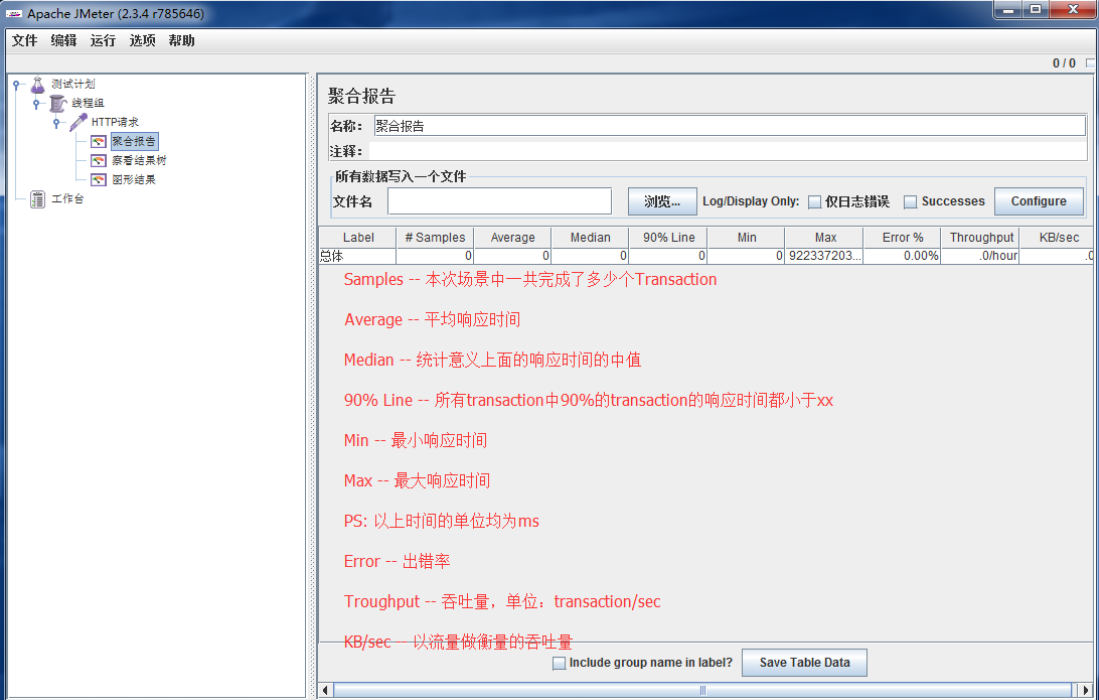
来源: Mongodb 与sql 语句对照 – 剑飘红 – 博客园
此处用mySQL中的SQL语句做例子,C# 驱动用的是samus,也就是上文中介绍的第一种.
引入项目MongoDB.dll
//创建Mongo连接
var mongo = new Mongo("mongodb://localhost");
mongo.Connect();
//获取一个数据库,如果没有会自动创建一个
var db = mongo.GetDatabase("movieReviews");
//创建一个列表,并为这个列表创建文档
var movies = db.GetCollection("movies");
连接没问题之后,现在让我们用mysql 与mongodb的一些语句做下对比:
| MongoDB | Mysql | |
| 查询全部 | movies.find(new Document()) | SELECT * FROM movies |
| 条件查询 | movies.Find(new Document { { “title”, “Hello Esr” } }); | SELECT * FROM movies WHERE title= ‘foobar’ |
| 查询数量 | movies.Find(new Document { { “title”, “测试2” } }).Documents.Count(); | SELECT COUNT(*) FROM movies WHERE `title` = ‘foobar’ |
| 数量范围查询 | 1, movies.Find(new Document().Add(“where“,newCode(“this.num>50“)));2,movies.Find(newDocument().Add(“num“,newDocument().Add(“where”,newCode(“this.num>50”)));2,movies.Find(newDocument().Add(“num”,newDocument().Add(“gt”,50))); (gt:>;gt:>;gte : >= ; lt:<;lt:<;lte : <= ; ne:!=)3,movies.Find(“this.num>50“);4,movies.Find(newDocument().Add(“ne:!=)3,movies.Find(“this.num>50”);4,movies.Find(newDocument().Add(“where”,new Code(“function(x){ return this.num > 50};”))); |
select * from movies where num > 50 |
| 分页查询 | movies.Find(new Document()).Skip(10).Limit(20); | SELECT * FROM movies limit 10,20 |
| 查询排序语句 | movies.Find(new Document()).Sort(new Document() { { “num”, -1 } }); | SELECT * FROM movies ORDER BY num DESC |
| 查询指定字段 | movies.Find(new Document().Add(“num”, new Document().Add(“$gt”, 50)), 10, 0, new Document() { { “title”, 1 } }); | select title from movies where num > 50 |
| 插入语句 | movies.Insert(new Document() { { “title”, “测试” }, { “resuleData”, DateTime.Now } }); | INSERT INOT movies (`title`, `reauleDate`) values (‘foobar’,25) |
| 删除语句 | movies.Remove(new Document() { { “title”, “Hello Esr” } }); | DELETE * FROM movies |
| 更新语句 | movies.Update(new Document() { { “title”, “测试2” } } , new Document() { { “title”, “测试11111” } }); |
UPDATE movies SET `title` = ‘测试1111’ WHERE `title` = ‘测试1111’ |
| Linq查询 | (from item in db.GetCollection(“movies”).Linq() where ((string)item[“title”]).StartsWith(“Esr”) select item); |
select * from movies where title like ‘%Esr’ |
这里只举出了几个比较典型的例子,可以这么说,只要mysql可以完成的sql语句,在mongodb里面都可以实现.
 Mikel
Mikel